 Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL

 Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL

In the technical market, developers are always searching for advanced data processing tools to process data faster to meet the flexible needs of the superior market. Also, advanced tools can handle real-time data processing within seconds. So first, let's get familiar with Spark. Apache Spark is getting quick momentum for enterprises and large-sized businesses with plenty of big data to work on.
The increasing demand for Apache Spark has triggered us to compile a list of Apache Spark interview questions and answers to help you complete your interview successfully. These questions are suitable for both fresher and experienced Spark developers to enhance their knowledge and data analytics skills. In fact, just for you, we have also created a dedicated and specialized SQL Server Certification training course, so you will never have to fear the interview.
Developers keep finding modern data processing tools to process data quickly and meet the flexible requirements of the market. The tools are effective in managing actual data processing in a concise period. So, Apache is gaining popularity in huge-sized enterprises with ample big data to work on. Let’s proceed to some Apache Spark interview questions to give you a better idea about the concept.
In the initial section, we will list 30 Spark Apache Interview Questions and Answers for 2024 to help you easily clear your interview. During later sections, we will answer each question by dividing the 30 questions into three sets – Apache Spark SQL interview questions, Apache Spark Scala interview questions, and Apache Spark Coding interview questions.
Each section shall contain many Spark Tricky interview questions that will give you that extra edge for the unexpected trivial questions by the interviewers.

Ans:- Here is a list of the key features of Apache Spark:
Among our various Apache Spark Interview Questions and Answers, it's important that you clearly understand this one as it forms the essence.
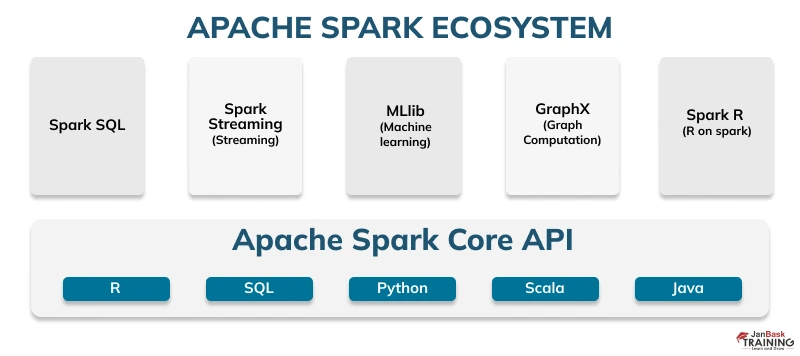
Ans:- Here are the core components of the Spark ecosystem:
Ans:- Apache Spark supports the accompanying four languages: Scala, Java, Python, and R. Among these languages, Scala and Python have intuitive shells for Spark. The Scala shell can be accessed through the ./canister/start shell, and the Python shell through ./receptacle/pyspark. Scala is the most utilized among them since Spark is composed in Scala, and it is the most prominently utilized for Spark. This is one of the prominent reasons that so many people like you constantly look out for Apache Spark interview questions.
Ans:- Apache Spark SQL is a popular ecosystem or interface for structured or semi-structured data. The multiple data sources supported by Spark SQL include text, JSON, Parquet, etc.
Ans:- MLlib is a versatile machine-learning library given by Spark. It goes for making machines adopt simple and versatile with normal learning calculations and utilizing cases like grouping, relapse separating, dimensional decrease, etc.
Ans:- Like Hadoop, YARN is one of the key highlights in Spark, giving a focal and asset administration stage to convey versatile activities over the group. For instance, YARN is an appropriate compartment supervisor, as Mesos, though Spark is an information-preparing instrument. Spark can keep running on YARN, similar to how Hadoop Map Reduce can keep running on YARN. Running Spark on YARN requires a parallel dissemination of Spark based on YARN support.
Ans:- Yes, Spark SQL helps in big data analytics through external tools too. Let us see how it is done, actually –:
Ans:- Spark SQL is an advanced database component able to support multiple database tools without changing their syntax. This is the way how Spark SQL accommodates both HQL and SQL superiorly.
Ans:- Real-time data processing is not possible directly, but obviously, we can make it happen by registering existing RDD as a SQL table and triggering the SQL queries on priority. Normally, it won't be that easy to explain it in-depth in these Spark Interview Questions and Answers for 2023, and i.e., why we recommend you to check our full fledged Online SQL training in India, where we shall explore this domain.
Ans:- RDD is an abbreviation for Resilient Distribution Datasets. An RDD is a blame tolerant accumulation of operational components that keep running in parallel. The divided information in RDD is permanent and distributed in nature. There are fundamentally two sorts of RDD:
RDDs are essential parts of information that are put away in the memory circulated crosswise over numerous hubs. RDDs are sluggishly assessed in Spark. This apathetic assessment is the thing that adds to Spark's speed.
This section will present a collection of carefully selected Apache Spark Interview Questions, which are aimed at testing your knowledge, problem-solving abilities, and Spark SQL skills regarding working with structured data. As these questions provide an overview of various topics from basic concepts to advanced techniques, this can give you a clear picture of where you stand to crack Spark SQL interviews.
Ans:- There are two types of operations that RDDs support: transformations and actions.
Ans:- Parquet is a columnar arrangement record upheld by numerous other information preparing frameworks. Start SQL performs both read and write operations with Parquet document and think of it as an extraordinary compared to other enormous information examination arranges up until this point.
Ans:- Parquet is a popular columnar file format compatible with almost all data processing systems. This is the reason why it is taken as one of the best choices for big data analytics so far. Spark SQL interface is able to perform read and write operation on Parquet file and it can be accessed quickly whenever required.
Ans:- Spark SQL is a parallel data processing framework where batch streaming and interactive data analytics is performed altogether.
Wanting to know more? Simply check out our SQL Server certification course, and get a good grasp over the concept of parallel or distributed data processing framework.
Ans:- Catalyst framework is advanced functionality in Spark SQL for automatic transformation of SQL queries by addition of optimized functions that help in processing data faster and accurately than your expectations.
Ans:- Each spark application has the same settled load estimate and settled a number of centers for a spark agent. The pile measure is the thing that alluded to as the Spark agent memory which is controlled with the spark.executor.memory property of the – agent memory signal. Each spark application will have one agent on every laborer hub. The agent memory is fundamentally a measure on how much memory of the specialist hub will the application use.
Ans:-To maintain query accuracy and response time in Spark SQL, you are advised to go with BlinkDB query engine. The engine renders queries with meaningful results and significant error to maintain the accuracy.
Ans:- The programming in Hadoop is really tough. It has been made easier with Spark by usage of interactive APIs for the different programming languages. Obviously, Spark is a preferable choice than Hadoop in terms of usage. But, still we have seen that the experienced readers going through our Apache Spark interview questions may be divided into two supporting stances. You can simply join our forum to express your ideas further, supporting the reasoning behind your stance.
Ans:- Spark has the ability to perform data processing 100 times faster than MapReduce. Also, Spark has inbuilt memory processing and libraries to perform multiple tasks together like batch processing, streaming, interactive processing etc. The above discussion makes sure than Apache Spark is surely better than any other data processing frameworks exist as of now.
Ans:- The Array is a mutable data structure that is sequential in nature while Lists are immutable data structures that are recursive in nature. Size of array is predefined while lists change its size based on operational requirements. In other words, Lists are variable in size while the array is fixed size data structure.
Navigating through the landscape of Apache Spark Scala interview questions, it is crucial to acknowledge the unique challenges they present. These spark tricky interview questions are tailored not just to gauge your understanding of Apache Spark but also to assess your proficiency in Scala, a language integral to Spark's operation. For those seasoned in the field, this compilation of Apache Spark interview questions and answers for experienced people serves as an indispensable tool for career advancement.
Ans:- The most wonderful solution to map data and forms together in Scala is “apply” and “unapply" methods. As the name suggests, the apply method is used to map data while the unapply method can be used to unmap the data. The unapply method follows the reverse operation of the apply method.
Ans:- Yes, it is possible that private members of Companion classes can be accessed through companion objects in Scala.
Ans:- Every time when working with concurrent programs and other similar equality issues then immutable design in Scala programming language works amazingly. It helps in resolving coding-related issues and makes programming easy for Scala developers.
Ans:- The keywords "def" and "this" are used to declare secondary or auxiliary constructors in the Scala programming language. They are designed to overload constructors similar to Java. This is necessary to understand the working of each constructor deeply so that the right constructor can be invoked at the right time. Even the declaration of the constructor differs from each other in terms of data types or parameters, and more about this we shall explore in the upcoming Apache Spark interview questions.
Ans:- Yield keyword can be used either before or after expressions. It is taken more useful when declared before expression. The return value from every expression will be stored as the collection. The returned value can either be used as a normal collection or iterate in another loop.
Ans:- In case, when we want to invoke functions silently without passing all the parameters, we should use implicit parameters. The parameters that you want to use implicit, you need to provide default values for the same.
Ans:- Scala trait is an advanced class in Scala that enables the use of multiple inheritances and it can be extended to multiple classes together. In other words, one class can have multiple Scala traits based on requirement. Traits are used commonly when you need dependency injection. You just need to initiate class with Scala traits and dependency will be injected immediately.
Ans:- Normal users are generally confused between two terms parallelism and concurrency in the Scala programming language. It's one of the Spark tricky interview questions that shall discuss in simple words how they are different from each other and their significance too. When processes are executed sequentially then it is termed as concurrency while processes are executed simultaneously then it is named as parallelism technology. There are several library functions available in Scala to achieve parallelism.
Ans:- If you want to understand Monads in simple words then it would not be wrong comparing them with a wrapper. As wrappers are used to protect any product and to make it attractive, Monads are used for the same purpose in Scala. They are used to wrap objects together and perform two important functions further. These functions are –
Ans:- Transformations are created early in programs and these are generally used along with RDD. These functions are applied on already existed RDD to make a new RDD. Transformations cannot be used without implementing actions in Apache Spark. The most popular examples of transformation are amap () and filter () that helps to create new RDD by selecting elements in available RDD.
In the realm of Apache Spark Coding Interview Questions, it is important to note that coding aptitude is a significant aspect of mastering Apache Spark. These questions are very carefully constructed to test your coding abilities, especially in the light of the distributed and computing framework that defines Spark. For professionals who want to prove their proficiency, these spark tricky interview questions are a true gauge of their coding capabilities and knowledge about Spark’s core features.
Ans:- The data is taken back to the local machine from RDD with the help of “actions” in Apache Spark. The popular example of the action is folded () passes value again and again until the time it is left only one. The actions are executed with the assistance of transformations that are created early in programs. The most popular examples of transformation are amap () and filter () that helps to create new RDD by selecting elements in available RDD.
Ans:- Spark Core in Apache Spark is used for memory management, job monitoring, tolerate faults, scheduling jobs and interactive storage features. RDD is an advanced feature in Spark Core suitable for tolerating faults. RDD is a collection of distributed objects available across multiple nodes that are generally manipulated in parallel.

Ans:- No framework can come to the top without the functionality of live data streaming or handling live events. This is the reason why Apache Spark has used the most advanced techniques to allow the same, as you would have already seen by now in our previous Spark Interview questions and answers for 2024. For this purpose, Apache uses complex machine learning algorithms and high-level functions like reduce, map, join or window etc. These functions push data to file systems and live dashboards further.
Ans:- Out of all, one attractive feature supported in Apache Spark includes graph processing. Spark uses advanced multimedia component GraphX to create or explore graphs used to explore data more wisely and accurately.
Ans:- Spark MLib is a popular library function in Apache Spark to support machine learning algorithms. The common learning algorithms and utilities included in MLib library functions are regression, clustering, classification, dimensional reduction, low-level optimization, advance level pipelining APIs, and collaborative filtering etc. The main objective of the machine learning algorithm is recommendations, predictions and similar other functions.
Ans:- Apache Spark is an advanced data processing system that can access data from multiple data sources. It creates distributed datasets from the file system you use for data storage. The popular file systems used by Apache Spark include HBase, Cassandra, HDFS, and Amazon S3 etc.
Ans:- The three popular cluster modes supported in Apache Spark include – Standalone, Apache Mesos, and YARN cluster managers. YARN is the cluster management technology in Apache Spark stands for yet another resource negotiator. The idea was taken from Hadoop where YARN technology was specially introduced to reduce the burden on MapReduce function.
If you are interested in knowing more about it, simply be a part of our Online SQL training program.
SQL Server Training & Certification

Ans:- Yes, the cluster management technology in Apache Spark is popular with the name YARN technology. YARN stands for yet another resource negotiator. The idea was taken from Hadoop where YARN technology was specially introduced to reduce the burden on MapReduce function.
Ans:- There are two popular techniques that can be used to create RDD in Apache Spark – First is Parallelize and other is text File method. Here is a quick explanation of how both methods can be used for RDD creation. val x= Array(5,7,8,9) val y= sc.parallelize(x) val input = sc.textFile(“input.txt”);
Ans:- The key distinction between Hadoop and Spark lies in the way to deal with processing: Spark can do it in-memory, while Hadoop MapReduce needs to peruse from and keep in touch with a disc. Thus, the speed of handling varies altogether – Spark might be up to 100 times quicker. Be that as it may, the volume of information prepared likewise varies: Hadoop MapReduce can work with far bigger informational indexes than Spark.
Ans:- This is one of the most essential Apache Spark interview questions and answers for 2024 that discusses the three cluster managers, which are as follows:
Apache Mesos has three main components namely :
Ans:- Apache Spark is mainly utilized for the following:
Ans:- Pair RDDs refer to the value pairs which are utilized to execute special tasks on RDDs in Spark. Pair RDDs let the user access every key in correspondence. They constitute a reduceByKey () technique that gathers information based on every key and a join () technique that mingles various RDDs according to the elements possessing the same key.
Ans:- Using the subtractByKey () function helps to eliminate the elements present in other RDD. At times in our Apache Spark interview questions, you may come across short answers, and that's totally fine. It's not always about getting everything right, but rather being to-the-point and correct.
Ans:- It constitutes a web-based UI to observe the cluster in standalone mode which displays the cluster and job statistics. The log output for every task is noted to the working directory of the slave nodes.
Ans:- Akka is used by Spark to schedule tasks. Every worker requests for work from the employer after registering and the employer assigns them the respective work. Spark uses Akka to promote communication through messages between the employer and the employees.
Ans:- High availability can be obtained in Apache Spark by using single node recovery with the local file and integrating StandBy Masters with Apache Zookeeper.
Ans:- RDDs are used as the data storage model to get fault tolerance in Apache Spark. RDDs adhere to lineage data that allows them to reframe lost partitions utilizing the data from other datasets. So, in case a partition of an RDD is missing on account of a failure, then that certain partition needs to be reconstructed utilizing the lineage data. Confused? Worry not, at times even our Apache Spark interview questions and answers for experienced can be daunting at first, but once you practice a little, you shall be good to go!
Ans:- The main parts of a scattered Spark application are:
Ans:- Spark operates on data in a special way. When spark needs to run on a specific dataset, it listens to the commands and writes it down to memorize it but it carries out all of these actions only when the ultimate output is demanded. When a change like a map () is called on an RDD the operation is not executed instantly. Transformations are analyzed and calculated once you carry out an action. This allows for the optimization of the entire data processing workflow.
Ans:- A part within a cluster which is able to carry out spark application code is termed as worker nodes. It constitutes various workers, configured using the SPARK_WORKER INSTANCES feature in the spark-env.sh file. In case the feature is not well-defined then only one worker will be launched.
Ans:- Spark refers to a scattered data processing engine used for usual purposes according to various situations. There are also libraries for SQL, ML and graph computation which can be utilized coherently in a system. Spark Engine is in charge of scheduling, assigning and monitoring the data application across the spark cluster, which we have already discussed in previous Apache Spark interview questions.
Ans:- Yes, it is possible to use spark Cassandra Connector as it allows connecting the Spark cluster to a Cassandra database, promoting smooth data transfer and proper analysis between both technologies.
Ans:- It refers to a data framework present in Apache spark that displays a distributed accumulation of structured information where there is a proper schema or structure for every record. The schema underlines the data type and format of every column present in the dataset.
Ans:- The differences between Spark SQL and Hive are as follows:
Ans:- BlinkDB is used to let the user trade off query accuracy for a shorter response time and facilitate communicative queries over huge data. This is done by running queries on the samples of the data and showcasing the outcome with proper error bars. If you feel that you want to further dive into BlinkDB, then just go ahead and subscribe to our industry recognized SQL Server Certification program.
Ans:- Scalar functions refer to the functions that return just one value for each row. It comprises built-in functions like array functions.
Aggregate functions return a single value for a cluster of rows and it comprises built-in functions like min(), max(), count().
Ans:- Dstream is an abbreviation for Discretized stream that refers to a group of Resilient Distributed Databases displaying a data stream. Dstreams can be made from sources such as HDFS, Apache Flume and more.
Ans:- Dstreams comprise two types of transformations namely stateless and stateful.
Stateless transformation means the processing of a batch that does not depend on the output of the earlier batch. Examples include operations like map() and filter().
Stateful transformations are dependent on the output of the previous batch to process the ongoing batch.
Ans:- The various sources to process real data from Saprk streaming component include Apache Flume, Apache Kafka, Amazon Kinesis. Once you carry on reading the Apache Spark interview questions and answers, you shall know more of the sources in detail.
Ans:- Dstream is the bottom layer of abstraction in spark streaming API. It refers to the fundamental abstraction offered by Spark Streaming. It consists of a long data stream, including either the input data stream gained from the source or the processed information fdeveloped by converting the input stream.
Ans:- They are the special entities in spark streaming that gather data from multiple sources and transfer them to Apache Spark. The main aim of the receivers is to fetch data from various sources and transfer it to Spark.
Ans:- Spark streaming has the transform function which let the developers use Apache Spark transformations on the inherent RDDs for the stream. The map function is utilized for an element to element transform. A transform is an RDD transformation whereas a map is an elementary transformation.
Ans:- Spark MLlib is a machine learning library made on Apache Spark. It offers a vast range of tools for ML tasks like clustering and classification. Key features comprise scalability, scattered algorithms and proper integration with the data processing abilities of Spark. If you carry on reading our Spark interview questions and answers for 2023, you shall know more about the features.
Ans:- Spark MLlib accompanies a number of machine learning algorithms. However, Classification, regression, clustering and feature extraction are the most popular machine learning algorithms supported by Spark MLlib.
Ans:- Supervised learning includes labeled data and the algorithm makes assumptions depending on the labeled data. Examples are classification algorithms.
Unsupervised learning includes unlabeled data and the algorithm detects patterns within that data. Examples are clustering algorithms.
Ans:- Spark MLlib offers various ways to manage missing data including dropping rows or columns where the value is missing, providing missing values with mean values and using machine learning algorithms like decision trees and random forests.
Ans:- Shuffling refers to the process of redistributing data across partitions that may promote data transfer across the executors. It occurs while uniting two tables or while executing byKey operations.
Ans:- The functionalities supported by Spark Core are :
Does this seem too short? Want to know about the functionalities in detail? Simply subscribe to our online SQL training, and know all about the functionalities!
SQL Server Training & Certification

Ans:- The different stages of persistence in Spark include the following:
Ans:- It is a disseminated graph processing structure that gives a high level API to execute graph computation on huge scale graphs. It let the user carry out graph computation as a set of transformations and gives optimized graph processing algorithms for graph computations like PageRank and Connected Components.
Ans:- The analytic algorithms offered by Spark GraphX include PageRANK, Connected Components, Label Propagation, strongly connected components and triangle count.
Ans:- Shark is a tool constructed for those from a database background with a view to access Scala MLlib potentials through a Hive-like SQL interface. It enables the user to run Hive on Spark providing affinity with Hive metastore and data. If you are confused on how to go about running Hive on Spark, feel free to subscribe to our online SQL certification program.
Ans:- This refers to the program that handles the execution of a Spark job. It runs on the master node and collaborates with the worker nodes for the dissemination of Sparkjob.
Ans:- In local mode Spark runs on just one machine but in cluster mode Spark runs on a distributed cluster of machines. Moreover, cluster mode is utilized to process huge data sets but the local mode is used to test and create datasets.
Ans:- The difference between reduceByKey() and groupbyKey() in spark is that reduceByKey() groups the values of an RDD by key applying a reduce function to every group but groupBykey() groups the values of an RDD by key.
Ans:- This is a distributed data set which is laid out into columns with certain names. To be more specific, DataFrame refers to the dispersed data range, arranged in rows and columns, as similar in a lot other Spark tricky interview questions. Every column comprises a certain name and a type and DataFrames resemble conventional database tables, which are organized and definite.
Ans:- A DataFrameWriter is a section in Spark that enables users to note the contents of a DataFrame to a data source such as a file or a database. It refers to an interface that is utilized to copy a Dataframe to the external storage system for example, file systems, key-value stores and others.
Ans:- Repartition () mingles the data of an RDD and properly redistributes it through a particular number of partitions but coalesce () decreases the count of partitions of an RDD without mingling the data.
Ans:- The instances where Spark is ahead of Hadoop in processing are as follows:
Ans:- The process to connect Spark to Apache Mesos include the below mentioned steps:
In our SQL Server Certification, we take a look at many of the Apache Spark interview questions and answers for experienced individuals, which even includes installation procedures.
Ans:- Users can run any Spark job within MapReduce using SIMR ( Spark in MapReduce), without the need for any admin authorisation. This way they can launch Spark jobs inside Hadoop Mapreduce.
Ans:- Yes, it is possible for Spark and Mesos to run along with Hadoop by launching each service on the machines. Mesos works as an integrated scheduler that provides tasks to Spark or Hadoop.
Ans:- Spark need not be installed while running a task under YARN or Mesos owing to the fact that Spark can carry out a task on top of YARN or Mesos clusters without changing the cluster.
Ans:- Hadoop MapReduce needs programming in Java, which is made easier through Pig and Hive. Catching the syntax of Pig and Hive is time consuming. Spark has proper APIs for various languages such as Java and Python making it more compatible to use than Hadoop.
If you are still confused, then reading more of our already listed Apache Spark interview questions shall make you more clear on what's easier to use between Hadoop and Spark.
Ans:- Spark utilizes Hadoop by two vital methods, one being storage and the second one being processing. Spark primarily uses Hadoop for storing data through its cluster management computation.
Ans:- The choice depends on the project scenario. Spark uses memory and a huge amount of RAM and needs a machine to give proper output. So, the choice differs according to the demand of the project.
Ans:- Apache Spark may not be effective for compute-intensive tasks and can intake huge system resources. Spark can also pose a threat for big data processing. It is also devoid of a file management system. So, it needs to be combined with other cloud based data platforms.
Ans:- No, it is not compulsory to install Spark on every node of a YARN cluster when running Apache Spark. The reason is that Apache Spark runs on top of YARN, hence it is not mandatory to do so. But, if you are still confused, then you may even drop in with your own personal Apache Spark interview questions doubts.
Ans:- No, it is not mandatory to do so. Apache Spark uses Hadoop HDFS because there is no separate storage in Apache Spark but it is not mandatory. The information can be stored in the local file system as well.
Ans:- PySpark gives multiple functions to handle missing values such as dropna(), fillna() and replace(), which can respectively remove, fill or replace the values which are absent in DataFrames.
Ans:- A shuffle refers to a costly operation in PySpark that includes distributing data across partitions and it is needed when uniting two datasets. Shuffle suually occurs when the information requires distribution over the cluster. At this time, data is copied to local disk and then transferred across the web.
Ans:- PySpark MLlib refers to a library for machine learning that offers a range of distributed machine learning algorithms. It helps the users to create machine learning models which can be utilized for jobs such as classification and clustering. If you want to know about classification and clustering, you can search for these terms among our Apache Spark interview questions and answers.
Ans:- PySpark can be integrated with big data tools like Hadoop. This can be performed with the help of connectors and libraries. It can be joined with Hadoop through the Hadoop InputFormat and OutputFormat classes.
Ans:- The map() alters each element of an RDD into one new element but flatmap() alters every element into various new elements which are finally flattened into one RDD. Also, flatmap maps a single input value and many output values but map maps to a single value only. This si the main difference between the two.
Ans:- A Window function in PySpark enables the tasks to be done on a subset of rows in a DataFrame, depending on a certain window specification. It calculates running totals, roll averages and other such calculations.
Ans:- Optimization methods used to upgrade Spark performance include the following:
Do you feel this wasn't enough? Want more depth on our Spark tricky interview questions? Simply be a part of our lively community forum, or you may even comment below!
Ans:- Data transfer can be managed while working with Spark in the following ways:
Ans:- There are a few points of differences between persist and cache. Users can specify storage level with the help of persist, whereas for cache users are forced to use the default line. Also, cache method saves the Spark RDD to memory while the persist method stores it to the storage level of the user.
Ans:- In case the user does not explicitly mention, then the number of partitions is taken to be the default level of parallelism in apache spark.
Ans:- Some mistakes made by the programmers while running Spark applications include the following:
We have just listed some of the mistakes as we have to cover other essential Apache Spark interview questions too. But, if you are interested to know more, simply check out our SQL training program.
Ans:- The usual wotkflow of a Spark program includes:
Ans:- Usage of broadcast variables eradicates the necessity to send copies of a variable for each task so that the data can be processed quickly. It also stores a lookup table to promote retrieval efficiency.
Ans:- A Spark library that offers safe and reliable file sharing at memory speed over multiple cluster frameworks is Tachyon. It refers to a scattered file system allowing secure data sharing over cluster nodes.
Ans:- The operation can be identified based on the return type :
Ans:- Spark RDD can be created using various methods using Scala and Pyspark languages, of which we have even discussed in our above Spark Interview questions and answers for 2024.
For instance, It can be developed by implementing sparkContext.parallelize(), from a text file, from a different RDD and Dataset. The data needs to be loaded from a file along with parallelizing data accumulation in memory to create an RDD.
Ans:- Sparse vectors consist of two corresponding arrays for indices and values respectively which are utilized to store non-zero entries to save space. It is mostly a vector consisting mostly zeros, and a minimum number of non-zero elements. It is a beneficial data structure to showcase the information that is more or less null or includes multiple zeros.
Ans:- Yes, Apache Spark can be run on Apache Mesos. Infact, Apache Spark when combined with Apache Mesos gives various benefits such as dynamic partitioning and scalable partitioning. Spark can also run on hardware cluster nodes very smoothly with the accompaniment of Apache Mesos.
Ans:- There are various methods to facilitate automatic clean-ups in Spark to handle the accumulated metadata. However, the clean-ups can be promoted by creating the parameter ‘spark.cleaner.ttl’ or by categorizing the long running tasks into various batches and noting the final results to the disk.
Ans:- Spark can effectively work on hardware clusters when accompanied by Apache Mesos.It helps in the scalable distribution of jobs over various instances of spark and promotes effective designation of resources between spark and other big datasets. The other benefits of utilziing Spark with Mesos consist of dynamic partitioning between Spark and other infrastructures and scalable partitioning between various Spark instances.
Ans:- Reinforcement learning comprises a part of machine learning which oincludes the way agents can take step to get the highest cumulative reward. Hence Apache spark is suitable for normal ML algorithms such as clustering and classification and not for reinforcement learning.
Ans:-
Ans:- Conventional debugging methods can be utilized to debug spark code like print statements and logging. The spark web UI can be used to observe the progress of spark jobs and carry out the execution process. A tool like Databricks can also be employed to promote debugging for spark applications.
Ans:- Spark applications run as free processes collaborated by the spark season object in the driver program. The cluster manager provides jobs to the worker nodes with one task in every partition. Repetitive algorithms apply operations to the data to gain from caching datasets through iterations.
Ans:- These are the methods to avoid overfitting in ML models. L1 regularization offers a penalty term proportional to the exact value of the model coefficients but L2 regularization adds a penalty term proportional to the square of the coefficients. L1 regularization is employed in choosing features but L2 regularization is used for smoother models. If you want to know the specific formulas for L1 and L2, then simply check out our forum for more informative Spark tricky interview questions.
Ans:- MLlib refers to the machine learning library in Spark. It aims to develop smooth and scalable machine learning and offers tools like ML Algorithms like classification, regression and clustering. However, Spark MLlib tackles large datasets by distributing the computation over various cluster nodes.
Ans:- Spark streaming handles caching through the spark engine’s caching mechanism. It enables us to cache data in memory to promote quicker accessibility and reusability in respective operations.
Ans:- The hardware needs to be benchmarked to decide the number of codes and the factors like memory usage needs to be considered to calculate executors for real-time processing through Apache Spark.
Ans:- Temp views in Spark SQL are linked to the spark session that made the view and will not be available when the spark session ends. On the other hand, Global temp views are not linked to any spark session but to a system database and remain available until the spark session ends.
If you want a more informative comparison, go ahead and enroll in the JanBask Training’s SQL server certification courses.
Ans:- Sliding window operation handles the flow of data packets between networks. It also encourages smooth data processing by breaking it into smaller fragments. A sliding window involves tuples being categorised within a window that slides across the data stream as per a certain time span.
Ans:- Spark streaming encourages the user to process data streams in actual project scenarios whereas Batch processing processes huge datasets at once in a batch. It is used to process historical or offline data. Spark streaming involves the data being included into analytics tools one by one but batch processing framework requires the dataset to be collected at a time and then included in the analytics system.
Ans:- Yes, apache spark offers checkpointing with the aim to check the fault tolerance and security of spark applications. It refers to the mechanism where Spark streaming application gathers the data along with the metadata in the fault-resistant system. Data checkpointing is required for fundamental functioning whereas metadata checkpointing is needed to heal from driver failures.
Ans:- DAG means Directed Acyclic Graph. It helps Spark to divide a huge scale data processing task into a simple, independent job which can be performed parallelly besides optimizing the job execution and attaining fault resistance. There would be limited vertices and edges and each edge from one vertice is pointed at another vertex serially. The vertices are the RDDs of spark and the edges are the operations to be executed on those RDDs.
Ans:-
Want to know more? Simply read our other Apache Spark interview questions and answers for experienced that discusses these and other similar concepts.
Ans:- The pipe method provides the opportunity to create various parts of occupations that can use any language as required according to the UNIX Standard streams. It further helps the programmer process RDD data through external applications. We often need to implement an external library in Data Analysis. The pipe operator helps us to transfer the RDD data to the external application.
Ans:- Spark gives an effective API called GraphX which allows Spark RDD to support graphs and graph based calculations as well. It is a new addition to Spark and a directed multigraph containing edges and vertices. It can also be utilized to demonstrate a huge variety of data structures.
Ans:-
def keywordExists(line):
if (line.find("my_keyword") > -1):
return 1
return 0
lines = sparkContext.textFile("test_file.txt"); isExist = lines. map (keywordExists);
sum = isExist.reduce(sum);
print("Found" if sum>0 else "Not Found")Ans:- These are the data frameworks of sparkSQL that offer JVM objects with all the advantages of RDDs with sparkSQL optimized execution engine. Spark datasets are the typed structures that show the structured queries along with the encoders. It is a robust, immutable range of objects laid out in a relational schema. The nucleus of the Dataset API is a term called encoder used to transform JVM objects to tabular view.
Ans:- Accumulators refer to the shared variables which are given through a commutative operation and used to execute counters or sums. Spark helps to develop an accumulator of any numeric type and offers the chance to add personalized accumulator types. Two types of accumulators can be created by the programmer. They are named accumulators and unnamed accumulators.
Accumulators is a dedicated concept that we recommend you to in our forum section where we discuss a variety of more Apache Spark interview questions.
Now that we’ve covered a list of frequently asked apache spark interview questions, both conceptual and theoretical, all is left for you is to start preparing to land yourself yor dream job role.
You can also enroll into our big data hadoop certification to learn more about the apache spark and big data hadoop ecosystem. Through this certification course, yo can gain the required skill of the Apache Spark open-source and Scala programming language. The knowledge of these essential skills will help you to ace any Spark-related interview.
So lets get your your dream job by acing your Apache Spark interview questions today!
Q1. How does JanBask's SQL Server course prepare for Apache Spark interview questions and answers for experienced professionals?
Ans: The SQL Server course at JanBask is intricately designed to cover essential SQL concepts, vital for addressing complex apache spark interview questions and answers for experienced individuals. The curriculum delves into advanced SQL features and data handling techniques, which are frequently tested in spark tricky interview questions. This comprehensive online SQL training ensures a robust understanding of SQL's role in big data, an area extensively explored in Apache Spark interviews.
Q2. What aspects of the SQL Server certification are relevant to Apache Spark interview questions?
Ans: Earning a SQL Server certification through JanBask's course equips you with in-depth knowledge and practical skills in SQL, directly applicable to various Apache Spark interview questions. The certification highlights your proficiency in SQL programming and data analysis, critical areas in Spark interviews. This alignment ensures that you're well-prepared to tackle the technical depth often encountered in Apache Spark interview questions and answers.
Q3. Can the online SQL training from JanBask help in answering Spark Interview Questions and Answers for 2023?
Ans: JanBask’s online SQL training is constantly updated to reflect current industry trends and technologies, making it a valuable resource for preparing for Spark Interview Questions and Answers for 2023. The course covers a broad range of topics from basic SQL commands to complex database management techniques, which are essential for understanding the latest developments in Apache Spark and big data technologies.
Q4. How does the online SQL certification support preparation for Apache Spark Interview Questions and Answers?
Ans: The online SQL certification from JanBask Training validates your expertise in SQL, a key component in Apache Spark. This certification demonstrates your capability to handle data-centric tasks in Spark, a common theme in Apache Spark Interview Questions and Answers. The comprehensive understanding you gain from this course will enable you to approach Spark interviews with confidence.
Q5. Are there any direct correlations between JanBask's SQL Server course and Apache Spark interview questions?
Ans: JanBask's SQL Server course is closely aligned with the core concepts often explored in Apache Spark interview questions. The course’s emphasis on SQL programming, database management, and data analysis provides the foundational knowledge and skills necessary to excel in interviews focused on Apache Spark’s data processing capabilities.
Q6. How does learning SQL at JanBask Training help with advanced apache spark interview questions and answers for experienced individuals?
Ans: For experienced professionals, JanBask’s course offers deep insights into advanced SQL topics, critical for tackling advanced apache spark interview questions and answers. The training includes practical examples and scenarios that mirror the complexity of problems often posed in Spark interviews, preparing you to address them with expertise and confidence.

Hive Interview Question And Answers


Splunk Interview Questions and Answers

Teradata Interview Questions and Answers

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment