Introduction
Do you know that AWS has more than 1 million active users and offers 175 fully functional services? AWS, a subsidiary of Amazon, is not only restricted in the ecommerce landscape. It has spread its wings into the cloud computing market and has fixed its place. AWS currently serves more than 190 countries worldwide making it the best in the global cloud computing industry.
The AWS S3 is one of its most powerful and reliable storage systems that enables users to store or retrieve data from anywhere. With global businesses dealing with large amounts of data, the need for cloud professionals are at its peak. Whether you are a novice in the I.T career or want to progress your cloud computing skills, a certification can add value to your resume. Our AWS Certification Course covers the fundamentals of AWS and its techniques, thus making you ready for the industry. The AWS S3 Tutorial shall discuss Amazon simple storage service with examples to give you a deep idea of the concept. As you know, voluminous data is produced every day that results in increasing storage requirements. It demands to maintain and build your own repositories; therefore, it becomes a tedious and boring job as the amount of overall storage capacity you exactly need in the future is tough to predict.
Keeping all these hurdles in mind, Amazon came up with a powerful internet storage service Amazon S3. We will take you on tour in this blog where you shall learn everything about the service in detail and its benefits for a business.
Willing to learn these technologies and brush up your skill sets, enroll for the best Cloud Computing certification now!
A Quick Introduction to Amazon S3
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is designed for the internet to enable large-capacity, low-cost storage provision across different geographical areas. It provides IT teams and developers with durable, flexible, and durable object storage. Before proceeding, you need to learn the basics of S3. Check out from this blog.
Topics to be covered in the introductory section:
- How is S3 Secure?
- How is S3 Durable?
- Data Storage in S3
- Storage Classes in S3
- Data Organization in S3
- Amazon S3 with Example
Let us discuss each of the sub-sections one by one below:
S3 is considered the most secure choice because of the following reasons:
- Data encryption for the stored data can happen in two ways:
- Client-side Encryption
- Server-side Encryption
- Multiple copies of data are maintained to enable the regeneration of data in case of data corruption.
- Also, versioning is performed wherein each edit is archived for potential retrieval.
S3 is Durable because:
- It verifies the integrity of stored data using a checksum. If S3 detects any corruption in data, it can be quickly repaired by using the data replication process.
- Every time data is stored or retrieved; it checks the incoming network traffic for corrupted data packets.
- Also, S3 is highly scalable in nature where storage requirements can be scaled automatically based on requirements, and you have to pay for what you are actually using currently.
AWS S3 is the primary object storage service of AWS Cloud Computing. Learn more on AWS object storage from this blog.
How is S3 Secure?
- Data encryption for the stored data can happen in two ways:
- Client-side Encryption
- Server-side Encryption
- Multiple copies of data are maintained to enable the regeneration of data in case of data corruption.
- Also, versioning is performed wherein each edit is archived for potential retrieval.
How is S3 Durable?
- It verifies the integrity of stored data using a checksum. If S3 detects any corruption in data, it can be quickly repaired by using the data replication process.
- Every time data is stored or retrieved; it checks the incoming network traffic for corrupted data packets.
- Also, S3 is highly scalable in nature where storage requirements can be scaled automatically based on requirements, and you have to pay for what you are actually using currently.
AWS S3 is the primary object storage service of AWS Cloud Computing. Learn more on AWS object storage from this blog.
After this discussion, the next question that hits your mind directly is what kind of data can be stored in AWS S3?
Virtually, almost any type of data can be stored with S3 in different formats. If we are discussing the capacity, the number of objects and volume that we can store with S3 are unlimited. An object is considered the basic storage entity in S3 that consists of a key, data, and metadata. So, Data can be divided into two categories further:
- Data that has to be accessed frequently.
- Data not to be accessed frequently.
Geographical Data Storage in Amazon S3
You can decide where your data should be stored geographically. Although making a wise decision for the region is necessary, yet it needs to be planned well. Four parameters could help you in deciding the optimal region for the storage. These are – Price, customer location, Latency, and service availability, etc.
Storage Classes in Amazon S3
Therefore, Amazon comes up with three storage classes to deliver the best experience to its customers at very affordable rates.

- Amazon S3 Standard for frequent data access: This standard is suitable for performance-sensitive use cases where the latency is kept low. For example, if we talk about a healthcare organization, then frequently accessed data will be of admitted patients that should be retrieved quickly.
- Amazon S3 Standard for less frequent data access: It is suitable for use cases where data is accessed less frequent and long-lived. In the same hospital, data for discharged patients is not required on a daily basis, but you may have to access it when the patient returns with any complication. In that case, the discharge summary for those patients should be retrieved quickly.
- Amazon Glacier: It is suitable for use cases when data has to be archived, but high performance is not needed in those cases. It costs lower as compared to the other two services. In a hospital, blood report, X-ray report, or MRI scan docs that are one year older, not required by healthcare organization an1). Compliance Capabilityymore.
If you are one of those who want to pursue a career in AWS, then this is the right place for you. This blog will answer your query on how to become an AWS Architect.
Data Organization in Amazon S3
Data in Amazon S3 is organized into buckets. A bucket is a logical storage unit in S3. It contains objects that contain the metadata. Before adding any data to Amazon S3, the user should create a bucket first that can be used to store objects ahead. Moving ahead, let us try to understand the Amazon Simple Storage Service with the help of an example below.
Amazon S3 with Example
Take an example of the Company that has to launch its storage instances to host a website for its customers in Indian and USA. To deliver the best customer experiences, the Company has to choose one region that suits the best its requirements.
| Regions |
Mumbai/N Virginia |
| Instance Type (Reserved Instance) |
e.g amazon ec2-m4.4xlarge 16(vCPU), 64 GM RAM |
| Pricing ( 1 Year) |
Mumbai -$691/monthly - $0.9 Hourly N Virginia - $480/Monthly - $0.6 Hourly |
| Latency |
Form USA to India –Low From India to USA -High |
Based on the above parameters, it is pretty clear that N Virginia is just a suitable region for the Company to host its website because of the low latency and the low price. Irrespective of your location, you may bid on other regions too that suits your requirements the best because there is always flexibility to access S3 buckets from anywhere.
Other than this, there are chances when the website is launched in another region, and backup is taken in another availability region. This feature is added recently to the Amazon S3 system and pretty much easy to use. To evaluate your skills, how much you know about the AWS platform and its technologies, take a quick quiz first.
Check out for more blogs and resources at JanBask Training and see how AWS can redefine your career!

Amazon S3 Benefits and Highlights
Amazon S3 has a set of benefits, and a few popular ones are stated below:
- Compliance Capability
- Flexibility Management
- Durability, Scalability, and Availability
- Systematic Work Approach
- Data Transfer Flexibility
- Large Data Storage
- Data archiving
- Backup & Recovery
Let us start with a brief introduction to each of the features one by one:
1). Compliance Capability
Amazon S3 supports three types of encryption. When it comes to auditing, S3 provides a secure integration with AWS Cloud trail to retain or monitor storage API call activities. Amazon Macie is an AWS platform that uses machine learning to arrange, secure, and discover the Aws data automatically. It also supports robust security standards and compliance certifications too. It helps the customer in satisfying compliance requirements for every regulatory agency virtually worldwide. If you are looking to begin a career in AWS check this comprehensive guide on AWS career path.
2). Systematic Work Approach
AWS S3 allows users to run big data analytics on a particular system without moving it to any other system. It allows users to retrieve the data back that was needed by S3 objects earlier. It allows users to convert a vast amount of unstructured data to a structured format with the help of SQL database programming language.
3). Flexibility Management
With the help of storage administrators, data can be arranged or visualized quickly. It helps in monitoring data sources and reduces the overall costs while improving the services. When Amazon S3 is used along AWS Lambda, it helps customers to log activities and many more functions without focusing on the infrastructure.
5). Data Transfer Flexibility
Amazon S3 uses plenty of ways for data transfer within the Amazon S3. It is possible with the help of an API that transfers data through the internet. There is one direct connection to transfer data within S3 that helps in data transfer to public or private networks. Aws snowball offers a data transfer system at the petabyte-level. There is one AWS Storage gateway that offers on-premises storage and helps in transferring data directly to the cloud through the premises of the user.
4). Durability, Scalability, and Availability
Amazon S3 is considered as one of the most durable storage services as it works on the global cloud infrastructure. Data has to pass through three physically available zones that are far away from the AWS region. It is available at most of the places and offers an effective way to design and operate databases or apps.
6). Data Archiving
Amazon S3 offers the facility to customers where data can be accessed quickly based on the need for compliance archives. To meet the system retention, Amazon Glacier provides “Write Once Read Much” Storage. There are lifecycle policies that make data transitioning between Amazon Glacier and Amazon S3 simpler and faster.
7). Large Data Storage and Analytics
The Company uses a large amount of data that can be stored in different formats in S3 buckets, and it can be used as a big data lake too for big data analytics. Amazon S3 provides us with many services that help us to manage voluminous data by reducing its costs and optimizing the overall speed of innovation.
8). Backup and recovery
As we have discussed already, S3 is highly durable and secure for data backup and data archiving. Also, it provides different S3 storage classes too that helps in optimizing data access and its performance while recovery time objectives. Read this AWS tutorial and get exposed to the basics of cloud computing.
Cross-region Replication in Amazon S3
Cross-region replication helps users either replicate or transfer the data to some other location without any hurdles. Obviously, it demands certain costs for its services that we will discuss in later sections. When compared to traditional data transfer schemes available over the web, AWS supports two popular mechanisms for data transfer.
These are Snowball and Transfer Acceleration. Transfer Acceleration helps in easy, fast, and secure data transfers over long distances by exploiting CloudFront technologies. CloudFront is a cache service by AWS where the data from client-side is transferred to the nearest edge location and further data is routed to the S3 bucket over an optimized network path.
Next popular data transfer scheme is Snowball that suggests the interesting idea of transferring data physically. Here, Amazon sends equipment to premises where you are free to load the data. It has a kindle attached to it with client’s address including when it was shipped from Amazon. When the data transfer process is complete on Snowball, Kindle will change the shipping address back to AWS headquarters where the Snowball has to be sent.
If you have large batches of data to move, then Snowball is just the perfect choice to consider. The average turnaround for snowball is five to seven days. In the same way, Transfer Acceleration can move up to 75 TB of data on a dedicated 1 Gbps line. It completely depends on the use case and you could take the decision accordingly. Moving ahead. Let us discuss the overall S3 pricing and how much it can cost you?
To work as an AWS Architect, you ought to utilise your skills and expertise for developing cloud computing solutions for your company. Read what are the roles and responsibilities of an AWS Solution Architect.
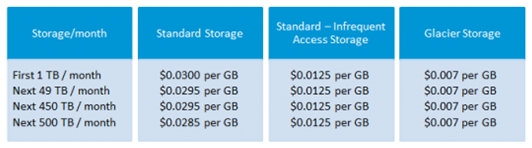
AWS S3 Pricing Structure
“Isn’t anything free on AWS?
If you are a beginner, then you can start with AWS S3 for free. Once signed up, new users get 5GB of S# standard storage, 20K Get-Requests, and 2K Put-Requests, 15GB of total data transfer each month for approximately one year. If you want to exceed this limit, then there is a certain amount that Amazon charges you. For this purpose, continue reading this blog ahead.
S3 has plenty of features; still, it is affordable and flexible when it comes to the payment. It allows you to pay for services that you are actually using. The below table will give you a better idea of S3 pricing for a specific region.

Here is a quick idea of how cross-region replication is billed:
If you replicate 1K objects, then you have to put requests to store 1000 objects and inter-region data transfer. Once data replication is complete, the 1000 GB will incur charges based on the destination region.
There are two variants of Snowball
- Snowball 50 TB: 200$
- Snowball 80 TB: 250$
These are the fixed service charges that you have to pay. Apart from this, you can check the website, and mostly charges are given exclusive of shipping days, shipping days are free. Transfer Acceleration pricing is shown in the following table:
Here, AWS S3 charges are quite manageable and affordable when compared to its benefits. You just have to understand which package suits you the most as per your requirements.
The adoption rate of AWS is the biggest reason why career opportunities and salaries of AWS professionals are soaring. Check out this blog on AWS Architect’s salary based on several factors.
Amazon S3 Use Cases
Case 1 – Industry Type – Media
Let us understand the concept with the help of a real-time example to assimilate what we have learned so far. IMDB is a popular internet Movie database to store details about movies, TV programs, video games, etc. Let us see how did they exploit the AWS Services to implement this movie database. To get the lowest possible latency, all possible outputs are calculated in advance with a document for every combination of letters in search. Each document is further pushed to the Amazon S3 and thereby to Amazon Cloud Front, and putting documents physically closer to users. The theoretical number of possible searches that can be calculated in mind-boggling. For example, a 20-character search has 23 x 1030 combinations.
In practices, by using the IMDB authority on movie and celebrity data, the search space can be reduced up to 150,000 docs and can be distributed in just a few hours.
Case 2 – Learn to host a static website on Amazon S3
Let us first learn, what is a static website? Have you any idea about it?
A website that only supports HTML, CSS, or JavaScript but server-side scripting is not supported. So, if you are looking to host a PHP app or Rails app, then you should opt for any other option. Moving ahead, let us dive deep to the wonderful world of hosting a website on AWS S3.
- Here, you have to create a bucket in the first step, navigate to the S3 in the AWS Management Console and hot the option “Create Bucket.” Here, you will be asked to give a bucket name and a region. If you want to add some subdomain, you can use it for the bucket name. For the region name, pick something nearest to you and hit “Create.” With a matter of instance, you can see that your bucket starts appearing in the console.
- Once the bucket is created successfully, it is the right time to verify a Bucket. Under “All Buckets” option, search for the bucket name you have created recently. If it appears in the list, it means the first step is completed successfully.
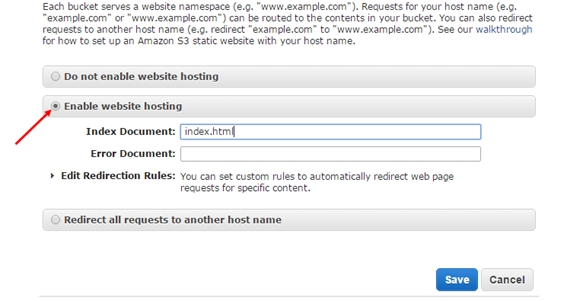
- In the next option, you should enable the Static Website Hosting. The only thing you have to do is, select the option from Properties panel on the right. The static website can be hosted entirely on Amazon S3. As soon as your bucket is enabled
- for the static website hosting, all the content is accessible through web browsers via Amazon S3 website endpoint for your bucket
 .
.
- In this step, you have to create an HTML file. Make sure that the index document is set to index.html. It is possible to set up an error page according to requirement. When you are done, just hit the “Save” option. One more nice thing about Aws Management Console is that you could upload files to your bucket right from the browser. Let us start by creating the index.htm page. Here is the HTML code for the same.
Start quizzing with this free Quiz on AWS and check your subject knowledge. It’s quick, fun and educational as well.
<title></title>
<meta name="description" content="My first S3 website"><meta charset="utf-8">
<body>
<h2>My first S3 website</h2>
<p>I can't believe it was that easy!</p>
<p>!doctype></p>
<ul>
<li>Now, we will learn how to upload a file in a bucket. To upload a file, you should select the new bucket option. However, it cannot be seen through the browser, yet everything in AWS S3 is private.<img alt="AWS S3 Tutorial Guide for Beginner " class="lazy img-responsive" data-src="https://assets.janbasktraining.com/blog/uploads/images/image_750x_5d36f0d41da69.jpg" src="data:image/png;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAD/ACwAAAAAAQABAAACADs="><img alt="AWS S3 Tutorial Guide for Beginner " class="lazy img-responsive" data-src="https://assets.janbasktraining.com/blog/uploads/images/image_750x_5d36f0ea0ca96.jpg" src="data:image/png;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAD/ACwAAAAAAQABAAACADs="></li>
<li>As we just discussed, everything in AWS S3 is private by default. So, you must be thinking about how to make it public to display on the browser. For this purpose, just right-click the index.htm file and select the “Make Public” option. Once it is set to the public option, the home page is visible to the world.<img alt="AWS S3 Tutorial Guide for Beginner " class="lazy img-responsive" data-src="https://assets.janbasktraining.com/blog/uploads/images/image_750x_5d36f15e0757f.jpg" src="data:image/png;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAD/ACwAAAAAAQABAAACADs="></li>
<li>Now select the index.htm file from the console and go to the Properties Tab.<img alt="AWS S3 Tutorial Guide for Beginner " class="lazy img-responsive" data-src="https://assets.janbasktraining.com/blog/uploads/images/image_750x_5d36f1722fa15.jpg" src="data:image/png;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAD/ACwAAAAAAQABAAACADs="></li>
<li>In the last step, you just have to verify the result. Paste the URL link on the browser and check if it is working or not. Yeah! It is that easy creating a website in S3. Hurray, we are done.<img alt="AWS S3 Tutorial Guide for Beginner " class="lazy img-responsive" data-src="https://assets.janbasktraining.com/blog/uploads/images/image_750x_5d36f18987ff8.jpg" src="data:image/png;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAAD/ACwAAAAAAQABAAACADs="></li>
<li>
<p>Congratulations, you have just hosted a website in AWS S3 with a few simple steps. Once a bucket is created, you can delete it; you can empty a bucket or move S3 objects from one bucket to another as required.</p>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
Object Lifecycle Management in S3
Amazon allows certain actions that can be automatically applied to objects stored within a particular bucket. These actions are attached as lifecycle sub-resources to the bucket and consist of the following actions:
- First is Transition action where objects can be moved from one storage class to another.
- Other is Expiration action where objects are removed automatically when they expire.
It is clear that transition actions are used to manage storage classes for objects within a bucket while expiration actions are used to delete an object automatically as soon as it expires. In this way, it is good if you want to store log files in your application for a certain time period only. When the defined timeframe will expire, log files will be removed as per the requirement.
Further, lifecycle management helps in moving objects from one of the real-time storage classes to the GLACIER class. Here are a few interesting facts you should know before you complete the data transfer process from one storage class to another.
- You can move one object to AWS Glacier, but it cannot be moved back to the standard library. If you want to do it, you should first restore the object hen copy the object subsequently with the storage class settings.
- It is not possible accessing objects moved from S3 bucket to the Glacier through Glacier API.
- Amazon stores each 8KB data block of information in S3 when you list all objects in the real-time.
- It may take up to 5 hours or more when objects are stored from Glacier as a temporary copy. The object will retain in Glacier until it is not deleted from that space.
Thinking of enrolling in an AWS Certification course? Here’s the ultimate guide AWS Training & Certification for a rewarding career ahead.
Encryption in Amazon S3
Encryption means encoding an object in such a way that only authorized users can decode that particular object. Basically, it is possible protecting the data when it is passed to Amazon servers and while the data is stored to the Amazon. Also, to protect the data during transmission, you can use SSL (Security Socket Layer) to transfer HTTP requests. With the help of Amazon’s Java SDK, it is possible to set up the protocol using “ClientConfiguration.” Here is an example for your reference:
ClientConfiguration clientConf = new ClientConfiguration();
clientConf.setProtocol(Protocol.HTTPS);
AWSCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = getAwsCredentialsProvider();
AwsEnvVarOverrideRegionProvider regionProvider = createRegionProvider();
return AmazonS3ClientBuilder.standard()
.withClientConfiguration(clientConf)
.withCredentials(credentialsProvider)
.withRegion(regionProvider.getRegion())
.build();
Data encryption for the stored data can happen in two ways: Client-side Encryption, and Server-side Encryption. Multiple copies of data are maintained to enable the regeneration of data in case of data corruption. Also, versioning is performed wherein each edit is archived for potential retrieval. In the case of server-side encryption, data is encoded before it is saved to the disc. Your client application managed the encryption process and sends the data that is already encrypted to Amazon. The best thing about server-side encryption is that Amazon has already encrypted the data and performed the key management for you.
Data will be in its original form for the moment while it is stored on Amazon machines. With the client-side encryption, you can encrypt your own application and learn to manage keys. This is the way how data is protected in the memory of your client’s machine and Amazon never sees the original content. Here, you have to focus on key algorithms and key management yourself.

Amazon offers three different types of Server-Side and client-side Encryption:
- Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3)
- AWS KMS-Managed Keys (SSE-KMS)
- Customer-Provided Keys (SSE-C)
- Client-side Encryption – KMS
- Client-side Master Key Encryption
- Versioning
Amazon S3 Managed Keys (SSE – S3):
Here, each object is encrypted using a unique key with the help of multi-factor encryption.
Further, a unique key is also encrypted with a master key that rotates regularly. This service uses Advanced Encryption standard for encrypting the data. Make sure that this encryption technique encodes only the object data, not the metadata.
AWS KMS-Managed Keys (SSE-KMS):
This type of encryption offers key management services that are designed to scale for large distributed apps. Here, the master key is created differently when compared to the SSE-S3 encryption process. However, both processes allow creating keys, define policies for them, and audit logs for the usage of each key. This is the default server-side encryption scheme used by the Amazon. The key can be used in subsequent calls unless you don’t specify another key.
Customer Provide Keys (SSE-C):
If you don’t like the idea that Amazon provides the key for data encryption, you have the flexibility to define your own key that is customer-centric key as the part of your requests. Further, Amazon implements the same key to encrypt or decrypt the data on the server-side. Amazon stores the HMAC value of the user-created key to validate future requests. In case, you lost the key created by your then HMAC value can help you to retrieve the same key and helps in robust key management.
Client-side Encryption - KMS
The server-side encryption techniques cannot be enough sometimes because Amazon knows the key value you are using, and there are certain points when raw data is in hand. To handle this situation, you can use KMS key and encrypt the data at the client-side. Here, the client first sends the request to KMS service to retrieve the data for encryption.
The KMS will suggest two random keys and returns the data in two different versions. The first version is used by the client, and the second version is the ciphered version of the data key. The ciphered version is sent as the metadata along with the encrypted data version to Amazon S3. When data is accessed, the client will load the encrypted and ciphered versions together. It then sends the ciphered version to the KMS service and receives the plain text as the decoded data object.
Client-side Master Key Encryption
Here, the client generates a random key to encrypt the data before the final upload. It then encrypts the data with a master key suggested by the client application and sends the encrypted data with a master key to Amazon. In this way, Amazon does have any idea about the raw data and the key used by the client for data encryption.
Versioning
To protect your data, from unwanted deletions or overwrites, you could enable versioning for a bucket. It will help in creating a new version of the object and upload the same version instead of overwriting the old data. Versioning is enabled on a complete bucket instead of any single objects. Once versioning is enabled, you cannot disable, but you can suspend it.
In this way, encryption is applied in different ways on client-side and server-side before data is sent to the Amazon S3. You can pick any of them as per your requirements and convenience.
Join our AWS community for more trending questions and latest updates from the members.
FAQs
Q1. What is AWS?
Ans- AWS or Amazon Web Services is a subsidiary of Amazon that specializes in cloud computing platforms that offer scalable and cost-effective cloud computing services. It provides distributed computing processing capacity and software tools to individuals and companies.This architect is the most flexible and secured cloud computing platform today.
Q2. What are the advantages of using AWS S3?
Ans- Here are the advantages of using AWS S3-
- Protects data
- Scalable
- Flexible.
- Easy to use.
- Data availability.
Q3. What are some of the features of AWS S3?
Ans- Some features of AWS S3are as follows-
- Storage management.
- Storage monitoring
- Data processing.
- Data transfer.
Q4. What exceptional benefits will I get from an AWS training online?
Ans- Our online training of AWS is not just about introducing you with theoretical knowledge for qualifying a certification exam, our motive is to deliver you the knowledge that can be practically applied. We serve you with the knowledge that's around real-industry scenarios, case studies & practical assignments along with theoretical practice. We unfold you with real-time learnings that will make you ready for real-time use cases of the AWS techniques.
Q5. What is the necessity of AWS certifications?
Ans- AWS certifications are important to have as they:
- Expand your job ready practical skills.
- Gives boost while representing portfolio & CV to recruiters.
- Maximize the possibility of getting hired over non-certified AWS Architects.
- Help you demand your desired salary, as AWS certification reflects you have proven competent skills.
- Help you get great confidence while dealing with AWS solution architect jobs or real industry projects.
Q6. What skills will I be learning in this course?
Ans- Here are all that you will learn:
- AWS Cloud Computing, AWS Architecture
- Identity Access Management & S3
- Amazon VPC, Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- Databases, Application Services, DynamoDB, Redshift
- Configuration Management, Automation, AWS Route 53
- Networking, Monitoring, Security Groups
Q7. What do AWS Developers do?
Ans- AWS Developers develop, migrate, and test AWS Cloud environments and integrate with other providers.They design and deploy solutions within AWS, while ensuring success during designing, building, and migrating applications, software, and services over the AWS platform and have robust use of services like EC2, EBS, Lambda, IAM, API Gateway, S3, DynamoDB, Elasticache, Step Functions, Kinesis, CFT, CloudFront, Load Balancers, AutoScaling, CloudWatch, CloudTrail, Elastic Search, VPC, etc.
Q8. What are the required skills for AWS?
Ans- Technical Skills for AWS Solution Architect jobs
- Java/Python or C++
- Networking
- Data Storage Fundamentals
- Security Foundations
- AWS Service Selection
- Cloud specific patterns & technologies
Personality skills for AWS Solution Architect jobs
- Communication Skills
- Time management skills
- Flexibility & eagerness to learn
- Business acumen
- Ability to stay agile
Q9. What can I expect after this course?
Ans- After completing our AWS certifications training online, you will achieve:
- Competent skills & knowledge, all ready to be utilized during the certification exam of AWS.
- Smart & well-calculated ways to proceed & absorb in the lucrative AWS led job markets.
- An AWS Training Certification online for training completion, by a highly recognized name - JanBask Training - declaring a successful completion of your learning-filled AWS training online for beginners to professionals. Our training completion certification gives you a great boost during interview calls.
Q10. What are the key concepts of S3?
Ans- The basic data map of S3 is bucket+key+version and the object itself. It is the combination of a bucket, an object key and a version ID that uniquely identifies an object.
Final Words:
At the final leg of AWS S3 Tutorial, we will recommend you joining the AWS certification program online at JanBask Training and know everything in depth from the beginning. We wish you luck for a successful career in the AWS space. All the Best!
AWS Course
Upcoming Batches
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
6 days 25 Jul 2025
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
6 days 25 Jul 2025
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
4 days 23 Jul 2025
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
6 days 25 Jul 2025
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
6 days 25 Jul 2025
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
13 days 01 Aug 2025
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
-0 day 19 Jul 2025
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
7 days 26 Jul 2025
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
6 days 25 Jul 2025
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
9 days 28 Jul 2025
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
6 days 25 Jul 2025
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
7 days 26 Jul 2025





 .
.




















