05
JulInternational Womens Day : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
AmazonS3 Simple Storage Service is an object storage service offered by a Web interface. It has various features like scalability, data availability, security, and performance. It was launched by AWS on 14 March 2006. It can be accessed and maintained through the internet.
The maximum limit for the number of S3 buckets that can be created per account is 100.
S3 consists of 2 main components:
It is now used by all the companies around the world, be it a small-scale industry or a large organization. S3 is helping these companies to keep safe their large data, which is further utilized for different devices/technologies like websites, phones. It is an object storage service and is different from block and file cloud storage.
Object has a combination of metadata and a unique ID number and is stored as a file. This ID number is used to access the object store in S3. This object can be accessed via REST api whereas the block cloud storage cannot be accessed.
AWS Solution Architect Training and Certification

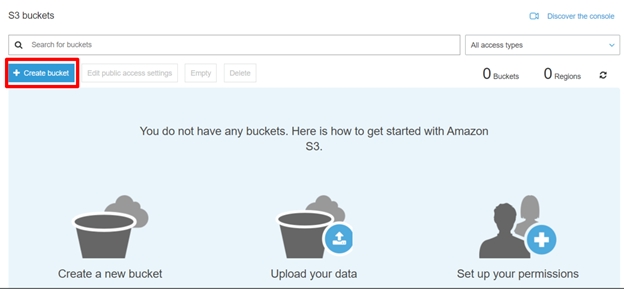
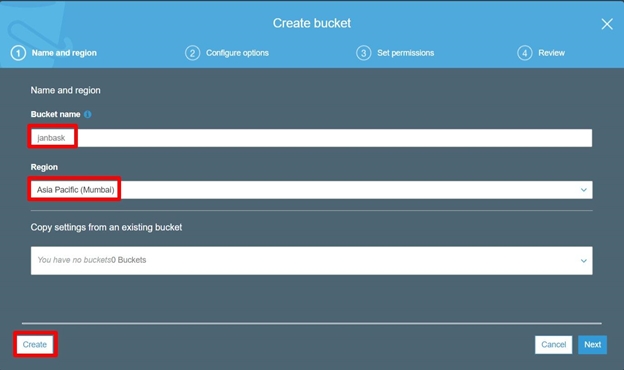
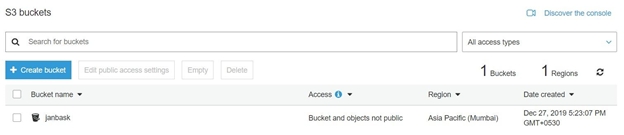
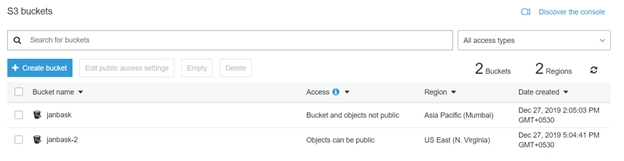
Let’s start by creating an S3 bucket.
Version control / Versioning
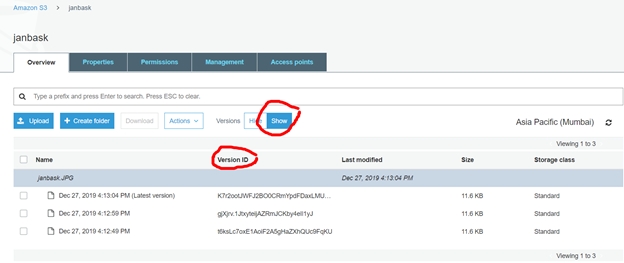
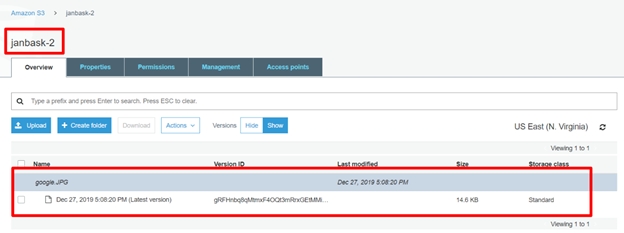
It helps in keeping different versions of the same object. Let’s take an example, of a picture (picture1) in a bucket and then we upload a new picture (picture1) with some changes in the same bucket, then the bucket will contain 2 versions of the same picture in this bucket. In case you want to revert back to the old image at some point of time, it helps here as you have all the versions of this picture saved in S3 and can successfully revert back to the old image. All the different versions of the pictures can be identified by the unique Version ID assigned to each picture.
How to Enable Version control?
It is set at the bucket level. Hence when we enable It for the bucket it is incorporated by all the objects stored in that bucket automatically.
It can be enabled using 3 ways:
1. AWS console - Graphical User interface provided by AWS.
2. SDKs - Allow developers to contribute towards these services using different tools and API’s.
3. API calls.- Different API provided by AWS can be used.
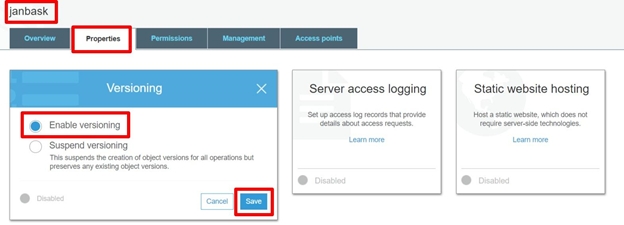
It provides a unique Version ID to all the objects uploaded in the bucket. This version is used to extract any specific object at any time using this unique version id.
Before the It is enabled, all objects will have “null” as the version id.
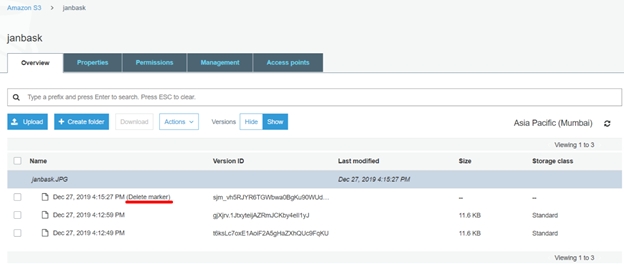
When we delete an object from S3, the versions of that object still remain in S3 but, a delete marker is inserted to the latest version of the object. Hence retrieving an object will give us a 404 error. Older versions of the object can still be retrieved using their respective version ids. Similarly, we can delete specific objects using their version id.
In such a case the next available version of the object will be set as the default version of the object.
Hence, the It starts as soon as you upload the object in the S3 that already exists, hence 2 versions appear in S3, making the latest object as the default version of the object.
When we upload any object is S3, it acts as a PUT request hence assigns a new version id to the object and setting
This is the default version id.
Read: What is AWS CloudFormation: Concepts, Templates, and EC2 Use Case
It helps us in protecting our data from getting deleted or overwritten.
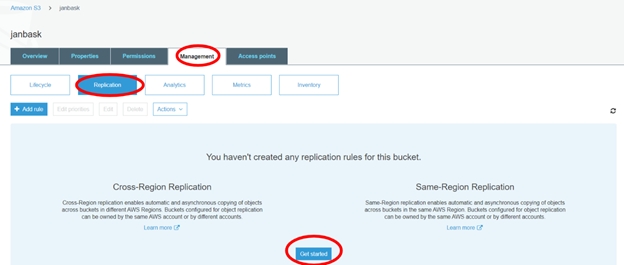
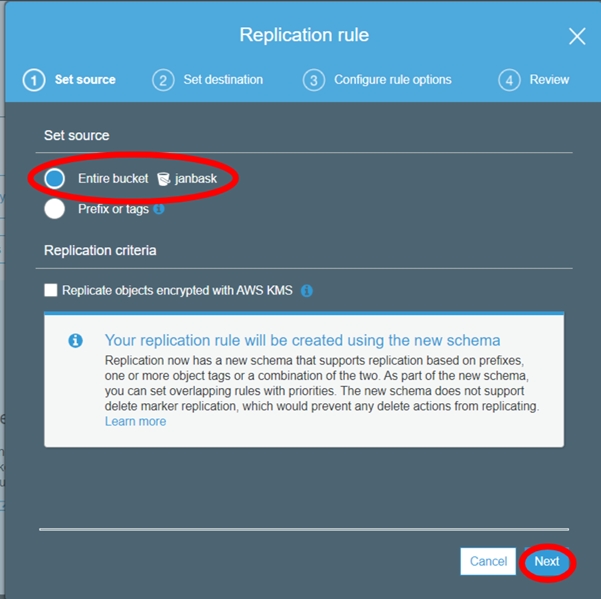
S3 Cross-Region Replication
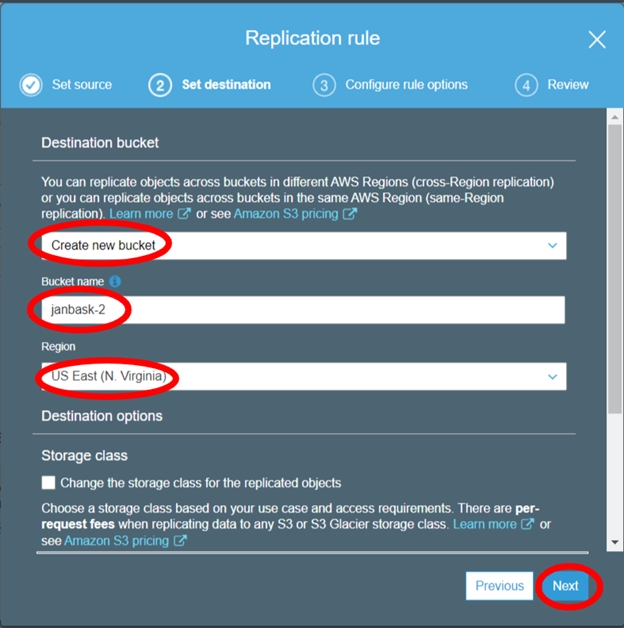
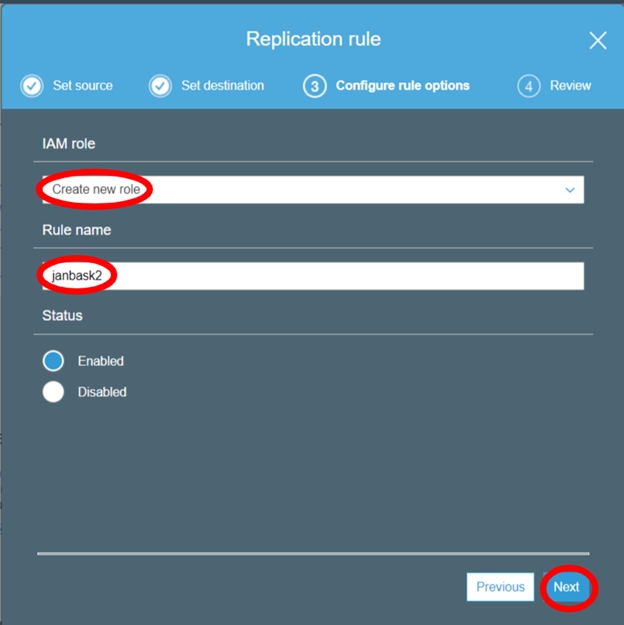
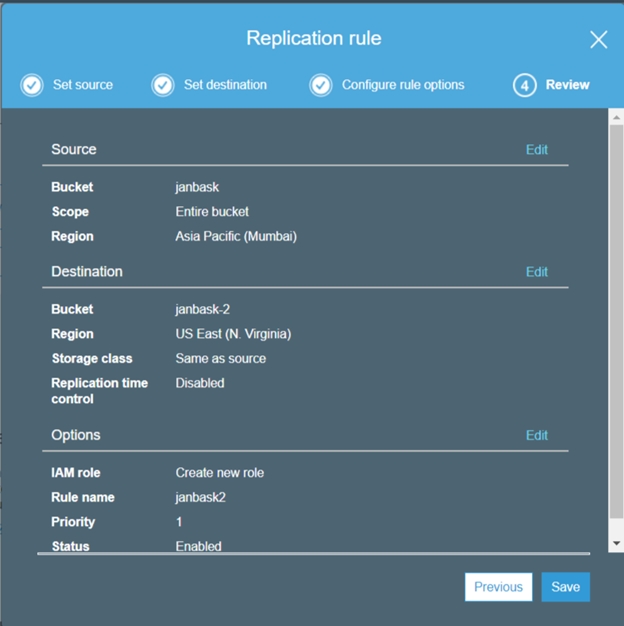
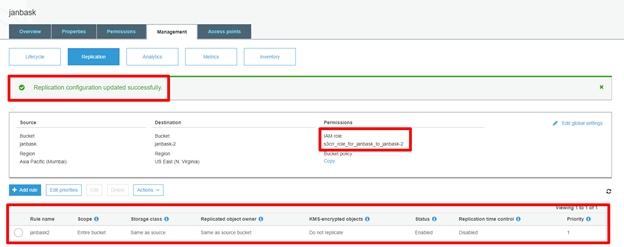
Cross-region replication is a feature provided by AWS, where our bucket data is automatically backed up in another destination bucket in any other AWS region. This action is performed automatically by AWS when we have the Cross-region replication enabled on any S3 bucket. A predefined destination bucket by us will be used for cross-region replication.
Objects that are copied in the destination bucket in another region have the same name and metadata as those in the parent bucket.
We can choose to replicate an entire bucket or only a specific data based on the prefix on type of data or file types.
Note- Objects added to the bucket after cross-region replication is enabled will only be replicated to the destination bucket and not the objects available before the cross-region replication option was selected.
Cross-Region replication needs at least buckets in 2 regions to work.
S3 It should be enabled in both source and destination buckets for cross-region replication to work properly.
Lifecycle policies need to be setup at the source and destination buckets to delete old data or to move them to Amazon Glacier.
To summarize:
1. Source and destination buckets are enabled.
2. Different regions selected different buckets.
3. Permission to S3 to replicate data between buckets.
4. Objects uploaded after CRR can only be replicated.
5. Replication can work only using 2 buckets.
Steps to setup cross-region replication.


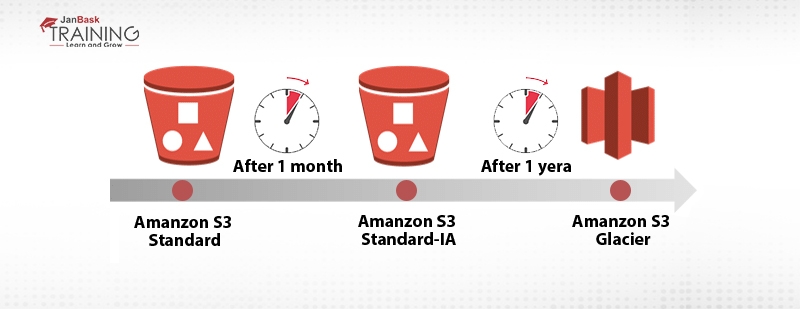
AWS provides large solutions for storage and one good option provided for cheap and storage of less frequently used data is Glacier.
It is best suited for data that consists of.
1. Large set of data that is hardly used or infrequently used.
2. Data that needs to be used after 6-7 years or more years gap.
Read: AWS DevOps Engineer Resume Examples & Templates
3. Data that is not immediately available and can be extracted or used after 3-4 hours of gap in retrieving it.
4. All kinds of data can be stored in AWS Glacier like image, text or zip files.
5. It can be scaled up and down as needed.
6. There is no limit to the data storage in AWS Glacier.
7. Data uploaded in stored in multiple availability zones.
8. Available as cheap as $0.01 / GB per month.
AWS Solution Architect Training and Certification

Inside AWS Glacier
Aws Glacier consists of 2 important part
Archives:
Any single content uploaded in glacier is called an Archive.
It is used to store data. Data of type image, videos, documents etc. can be stored here.
Direct content or multiple files compressed as Tar and Zip can be uploaded here.
Important things about Archives:
Vaults:
The collection of Archives in a glacier is called a vault. Vault is used to store multiple archives.
Important things about Vaults:
Amazon Glacier features:
Objects can be controlled or managed so that they are cost effective. This can be achieved using life cycle management rules or policies.
It covers 2 types of actions:
Read: Grow your career with these Top 10 AWS Influencers/ Cloud Computing Leaders
Transition - Movement of an object between different storage classes. Movement of object: Storage class A >> Storage class B.
Example: Object: Standard > Standard IA >> Glacier.
Expiration - Delete an expired object,after a specific number of days. It defines when an object is expired and hence is deleted from S3.
Create an image like:
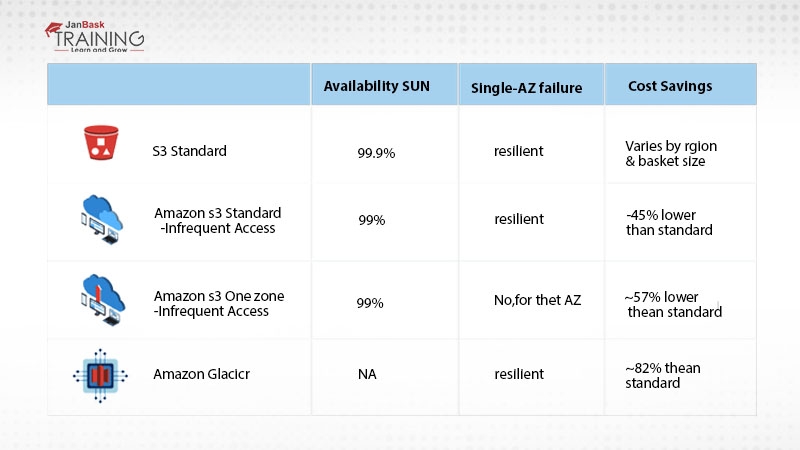
With multiple AWS storage option available today, we can choose between these different storage options based on the factors like:
With versioning enabled, large numbers of versions of a single file can be created which can become difficult to manage together.
Now with life cycle management rules we can save the cost by moving the less or infrequent accessed objects from Standard storage class to Standard Infrequent access or even rarely accessed objects to amazon Glacier. These policies or rules can be applied to objects older than 30 days or more.
1. Versioning should be enabled.
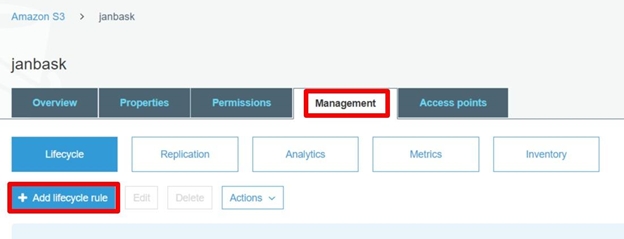
2. Go to Management > Add Lifecycle Rule
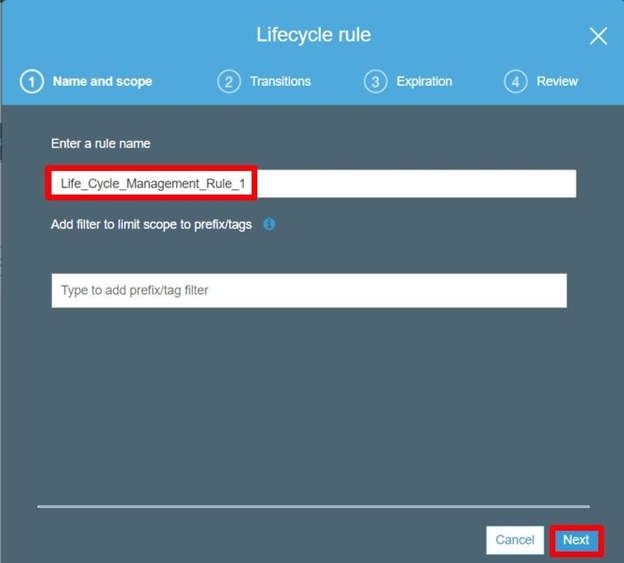
3. EntertheRule Name then click Next.
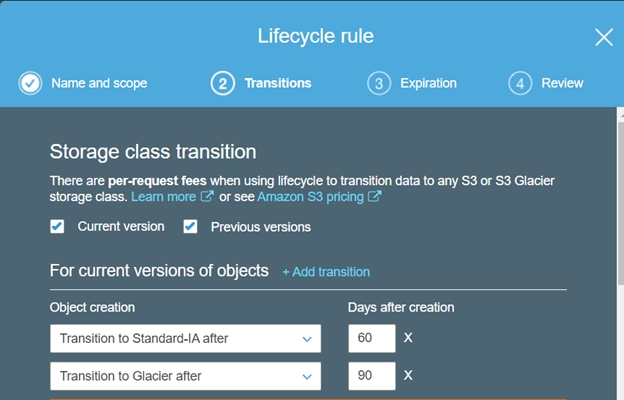
4. CreateTransitionrules for Current and Previous versions.
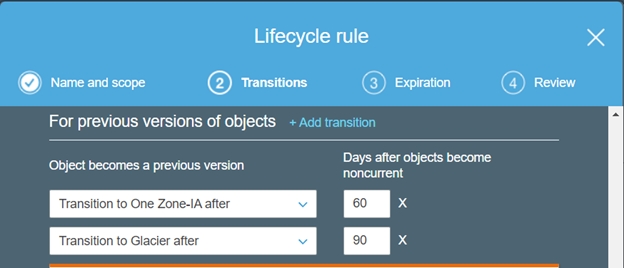
5. Select the values for the Expiration rule.
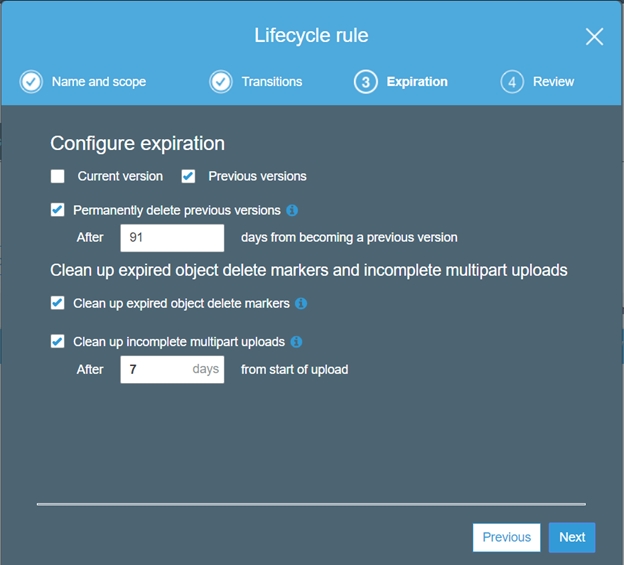
6. Review and save the Lifecycle management policy.
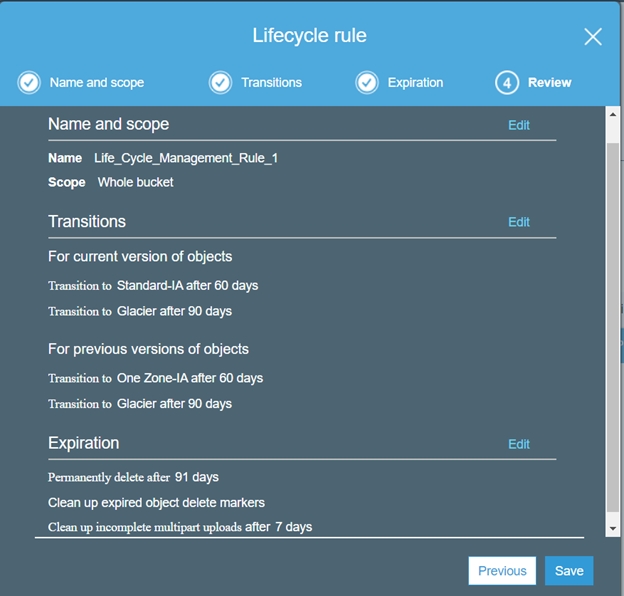
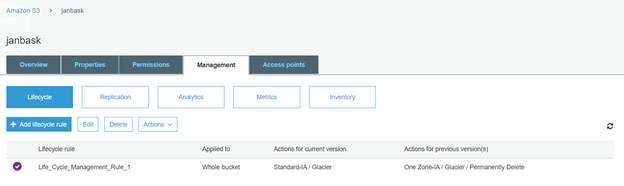
Conclusion
With the above write-up, we have learned the basics for Amazon S3, Glacier, and Life Cycle Management. We have practically created an Amazon S3 bucket. You can also create yours by following the above-mentioned steps. Let us know if you have any questions.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
A dynamic, highly professional, and a global online training course provider committed to propelling the next generation of technology learners with a whole new way of training experience.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on AWS Course
Interviews