11
JulGrab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Welcome to the world of SQL Server and its powerful functions! Data has become integral to every business in today’s digital era. For years, people have used SQL Server, a relational database management system, to manage and store their data.
One of the key features that make SQL Server so powerful is its ability to handle complex tasks through its functions. Functions in SQL Server are a set of SQL statements that perform a specific job, promoting code reuse and improving efficiency. With the help of functions, you can accomplish the same action repeatedly without writing lengthy SQL scripts.
In this blog, we'll look at the many kinds of functions that SQL Server offers and how they might make coding easier. Let's explore the SQL Server functions now!
Before learning about types of functions in sql server, you must also understand what is sql server afterall?
Microsoft created the relational database management system (RDBMS) SQL Server. It is used to organize data storage and management, and it supports SQL (Structured Query Language) for data management and querying.
Small-scale apps and large-scale enterprise systems use SQL Server in various applications and sectors. Data encryption, backup and recovery, replication, and reporting services are just a few of its services.
C++, C#, Java, Python, and other programming languages are supported by SQL Server. It is a frequent choice for managing massive, data-intensive systems and is widely used in web development, corporate analytics, and data warehousing.

SQL databases are within the group of database management systems known as relational database management systems (RDBMS), which employ SQL for data administration and querying. It is widely utilized in various applications, from modestly sized programs to massive business systems. Following are some of the primary characteristics and applications of the SQL database:
SQL Functions are programs either developed by the user or already provided by the SQL Server system which can be used to perform certain repetitive tasks.
“System-specified functions” are the functions that the system defines. In other words, system-defined functions refer to all the built-in SQL server functions supported. These functions typically use the SQL select statement to calculate the values and handle the data. Using the built-in features allows for significant development time savings when carrying out specific activities.
“User-defined functions” are often referred to as “functions that are developed by the user or developer in the system database or a user-defined database.” The user-defined functions may consider necessary parameters, carry out specific tasks, and return the data that has been processed.
By encapsulating the complex business logic and making it available for reuse whenever equivalent functionality is needed, these custom functions aid in the simplification of the database development process as a whole.
The user-defined functions make it much simpler to build the code required to query data. Additionally, it enhances the functionality, clarity, and accessibility of queries and enables other developers to reproduce the same processes appropriately. User-defined functions are those that a database user defines. The two sorts of UDFs are:
In order to use the uder-defined functions in sql server, you must know the correct syntax and practices for your functions to run smoothly. There are many top best-rated SQL books for beginners and advanced learners that talks about the usage of SQL functions in length. Here are some of the best practices compiled that must be followed:
You cannot alter, drop, rename, or aggregate a function if it is not created. To drop a function in SQL, you either need to ALTER permission on the Schema to which the process belongs or CONTROL permission on the function. To re-create a function, CREATE FUNCTION permission and ALTER approval on the Schema in which the function is created. With this discussion, you know how to make a function in T-SQL. Now let us discuss how to alter, drop, rename, and aggregate SQL functions.
To rename a function SQL Server, you can use either SQL server management Studio or Transact-SQL. When you rename a user-defined function, it will not change the corresponding object name in the definition of a function. So, it would be best if you dropped or recreated a function in that case instead of renaming it. Also, changing the name of the user-defined function can affect the performance of the attached objects too.
The dependent things may stop working when the function is loaded again. Let us see how to rename a user-defined function in SQL SERVER MANAGEMENT STUDIO.
This method cannot be used for the T-SQL database. To rename a T-SQL function, you first have to delete it and recreate it with the new name. Ensure that app applications and programs using the older function are now connected with the new one.
Here, we will learn how to ALTER a function created using the CREATE statement by changing its permission and affecting the dependent functions, stored procedures, triggers, etc. Here is the basic syntax for the ALTER command in SQL.
ALTER command cannot be used to change a T-SQL function to a CLR function or vice versa. ALTER function cannot be used to change a scalar-valued function to a table-valued function. Also, ALTER function cannot be used to change the INLINE function with multiple statements.
As we discussed, functions are created using the CREATE function and modified using the ALTER function. The DROP command is valid for existing functions only. The basic syntax for the drop command is given below.
Here, you can add the schema name to which the function belongs and the name of a user-defined function to be removed. Adding the schema name is optional, but the server name or database name cannot be specified here. DROP function does not work if it is bound with a Schema binding clause. It will not work if computed columns that reference this function are indexed. To execute the DROP function, you should add ALTER permission on the Schema to which it belongs or CONTROL permission on the function.
An aggregate function calculates a set of values and returns a single value. An aggregate function is generally used with the GROUP BY clause of the SELECT statement. It ignores null values too. They are deterministic and return the same value every time they are called for a specific set of inputs. There are certain cases where the aggregate function should be used as an expression. There are multiple aggregate functions in SQL, and you may use any one based on requirements. A complete range of aggregate functions in SQL is given below.
Similarly, SQL offers a complete range of in-built functions to perform operations on data. They are useful for mathematical calculations, string concatenation, sub-strings, etc. Each has a different syntax and is generally picked based on the analysis you want to perform with a function. If they are not used correctly, the final output differs from your expectations. So, it is necessary to understand the function of SQL Server and learn to use them effectively with basic syntax and argument knowledge.
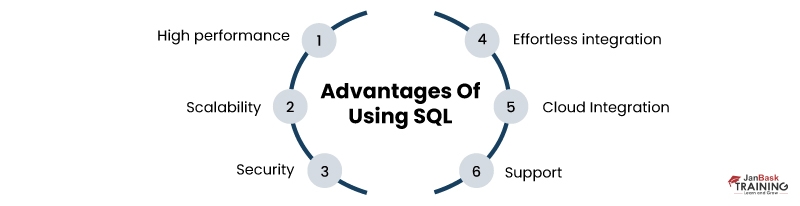
Microsoft’s relational database management system (RDBMS), SQL Server, has several benefits, including:
SQL database offers a range of features essential for managing and storing data efficiently. It is the best option for enterprises of all sizes because of its scalability, security, and backup and recovery options. Its reporting services, full-text search, and XML support features make it popular for web development and e-commerce applications. Its spatial data support feature makes it an essential tool for mapping and geolocation applications. To know more about SQL database, join our sql dba training to gain hands-on experience in working with real-world projects and be industry ready!
Q1. What are different types of SQL functions?
A1. In SQL Server, there are three types of user-defined functions
Q2. How to get all functions in SQL Server?
You may use the transact SQL command on system objects such as Sys. Objects, Information_Schema. Routines, syscomments, or Sys. Sql_Modules to retrieve a list of all the functions in a database.
Q3. What is the syntax for function in SQL Server?
To construct a function in SQL Server (Transact-SQL), use the following syntax:
CREATE FUNCTION [schema_name.] function_name ( [ @parameter [ AS ] [type_schema_name.] datatype [ = default ] [ READONLY ] , @parameter [ AS ] [type_schema_name.]
Q4. What is schema in SQL?
A schema is a list of logical data structures in a SQL database. The schema, which has the same name as the database manager, is owned by a database user. As of SQL Server 2005, a schema is a separate entity (container of objects) from the person who creates the item.
Q5. How many aggregate functions are there in SQL?
There are five aggregate functions in SQL,. These functions are as follows: MIN, MAX, COUNT, SUM, and AVG.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on SQL Server Course
Interviews