Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
IIF is one of the logical Transact-SQL functions that returns one among the two values based on the boolean expression. On the other hand, CASE is a language expression that assesses a list of conditions and returns one among multiple values based on the boolean expression. IIF is for single if-else conditions, and the case statement is for multiple conditions. There is a third function called Choose in SQL Server(). This returns the item from a list of items at a specified index. Let us cover each statement in detail, be it iff sql, switch sql, or case statement in SQL Server.
IIF() function in SQL Server returns one of two values, be conditional on whether the Boolean expression assesses to true or false in SQL Server.

SQL Server IIF syntax
The syntax for iif in SQL is as follows
IIF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)
The IIF() function always returns a value if the condition is TRUE, or another value if the condition is FALSE.
As mentioned, the IIF() function is based on the CASE expression. It, therefore, has the same limitations as the CASE expression (such as only being able to nest to a maximum level of 10).
Use of SQL Server IIF
The SQL IIF() function returns a value if the condition is TRUE or another value if the condition is FALSE.
IIF Statement in SQL Server Example
Let us take the case of the Adventurework database. The table that we will be using for this particular example is Employee.
Below is the query to view the table data
select * from [HumanResources].[Employee]
and below is the output

There is a field that holds the marital status of a particular employee. In the case of married, it shows M, and in the case of Single and S.

We will write a query using the SQL IIF statement, showing married if it is M and Single if it finds S. The query looks below.
Select Emp.BusinessEntityID, Emp.NationalIDNumber, Emp.LoginID, Emp.OrganizationNode, Emp.OrganizationLevel, Emp.JobTitle emp.BirthDate, iif(emp.MaritalStatus='M', 'Married,' 'Single') MaritalStatus from [HumanResources].[Employee] Emp
The output looks like the below
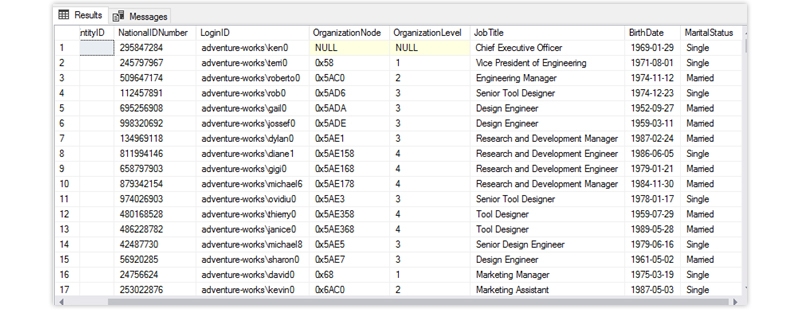
The CASE statement goes through various conditions and returns a value when the first condition is met (like an if-then-else statement). So, once a condition is correct, it will stop reading further and return the result. If no conditions are correct, it returns the value in the ELSE clause.
If no ELSE part exists and no conditions are proper, it returns NULL.

SQL Server Switch Statement Syntax
The SQL Switch case syntax is as below
CASE WHEN condition1 THEN result1 WHEN condition2 THEN result2 WHEN condition THEN result ELSE result END;
Advantage of Switch in SQL Server
The use of CASE tools results in goodish enhancements to quality. This can be primarily thanks to the fact that one can effortlessly retell through the various phases of code development, and therefore the possibilities of human error are significantly reduced.
Performance of Switch in SQL Server
Queries with multiple case statements encounters performance issues, as using multiple case statements tends to slow the query.
SQL Server Switch Case Statement
Let us take the case of the Adventurework database. The table that we will be using for this particular example is Employee.
Below is the query to view the table data
select * from [HumanResources].[Employee]
and below is the output
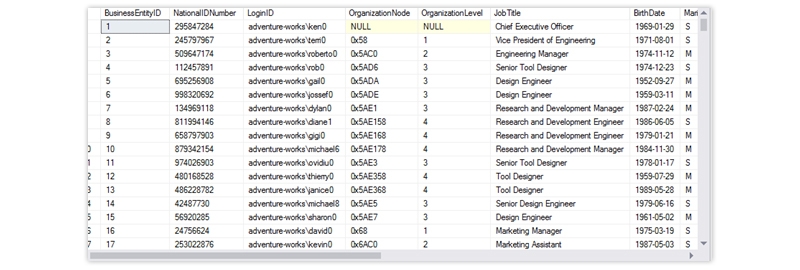
There is a field that holds the marital status of a particular employee. In the case of married, it shows M, and in the case of Single and S.

We will write a query using the IIF statement, showing married if it is M and Single if it finds S. The query looks below.
Select Emp.BusinessEntityID, Emp.NationalIDNumber, Emp.LoginID, Emp.OrganizationNode, Emp.OrganizationLevel, Emp.JobTitle, emp.BirthDate, case when Emp.MaritalStatus='M' then 'Married' when Emp.MaritalStatus='S' then 'Single' End [MaritalStatus] from [HumanResources].[Employee] Emp
The output looks like below
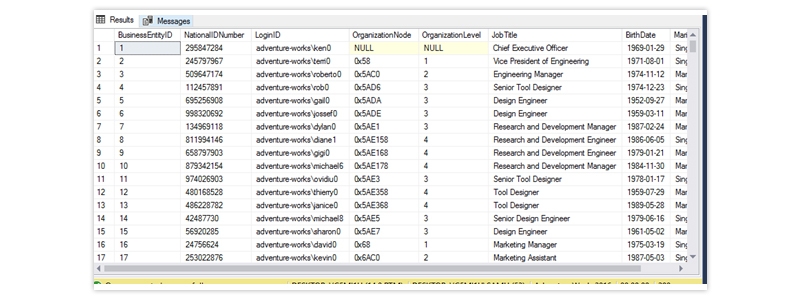
Choose SQL Server Function
We use Choose () function to return an item at a particular index position from the list of items. Syntax of Choose function: CHOOSE ( index, value[1], value[2] ,….. value[N] ) Index: It is an integer that specifies the index position of the element we want in the output.
SQL Server Choose Syntax
The syntax for the SQL Server Choose function is as below
CHOOSE ( index, val_1, val_2 [, val_n ] )
CHOOSE statement acts like an index into an array, where the array contains the arguments that follow the index argument. The index argument makes sure which of the following values will be returned.
Following is the SQL query for the sample choose function
SELECT CHOOSE ( 2, 'Microsoft,' 'SQL', 'Server') AS Output;
The output looks like below


SQL Testing Training
The blog documents the three most common conditional functions of SQL Server, iif, case, and chose. It describes its advantage and disadvantage with proper examples and syntax. It also shows how to use these tools with live examples. This reading will interest those who want to learn more about these three topics.

Database Files-Heart of SQL Server Database

Data Definition Language (DDL) Commands in SQL

What is Schema in SQL With Example: All You Need to Know

Different Types of DBAs and Their Roles

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Download Syllabus
Get Complete Course Syllabus
Enroll For Demo Class
It will take less than a minute
Tutorials
Interviews
You must be logged in to post a comment