25
JulGrab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Grab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Business environments are undergoing continuous change. There is an increase in uncertainties and unforeseen challenges emerging from the complexities of the hyper-connected world economy. The pace of development is presenting a compelling case to revise and revisit your business strategies constantly. There is an increased convergence of digital and social spheres, and there can be no isolated strategy to deal with either. The ground rules say, “Innovate or perish.” Survival is for the ones who stay on frontlines of innovation and is continuously churning new products.
This has made the role of a business analyst highly challenging and intuitive. He has to have a deep understanding of business value propositions, foster a spirit of innovation, and maintain a constant focus on product value. Realizing the above can actually mean that the difference which will decide success or failure for the organization as it walks through the challenges posed by the 21st century.
A Business Analysis Framework is a conceptual blueprint which describes all the vital requirements for getting the business done. It is based around knowledge utilization, various techniques which comprise the process and also the critical analysis. All these are essential for the analyst to boil down to the primary pain point of the business and also emphasizes various business enhancement opportunities. It also ensures a step-wise approach is implemented to tailor your business practices to the organization.
The domain of business analysis is highly diverse. There is a continuous rise in the number of business process requirements and customer expectations, both spurred by changing business landscape flushed in by technical breakthroughs. The framework provides a respite from the buzz around as a trusted source which can help you tide your business through rough waters.
Learn Business Analyst in the Easiest Way

It is evident that every organization has a specific process of business analysis. It helps in identifying and validating the business solutions to see if they can meet the business needs and objectives.
It is the primary responsibility of the business analyst to develop a deep understanding of the business process and document the same. It is a highly empowered role, and he or she is entrusted with many business secrets. A business analyst will seek to understand the basic structure of the business organization and process. Further, he or she will try to identify the areas of improvement or weak-links which have been generally overlooked. Once his groundwork is done, he or she now needs to be the most active participant of all the business meetings and clearly convey the business process to the development teams. Even after the product launch, he or she has to ensure that the product is matching the customer expectations. Also, it is important to note that a BA will have a key role at the beginning of product development as he or she has to actually translate the product requirements to the development team and further on will work in complete coordination with them to ensure the requirements are properly communicated and interpreted.
Here the intention is to highlight the primary causes of product failures. A product or project is categorized as a failure if it isn’t able to meet the expectations and the defined criteria. One has to compare the final product as per the business use cases. Here are some of the well-known causes of product failures:
A business analyst is required to be well-versed with some of the best techniques at hand. Here is a list of them:
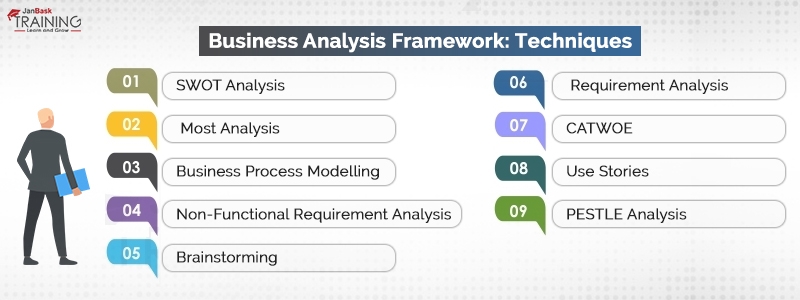
As the name suggests, the term SWOT stands for four components:
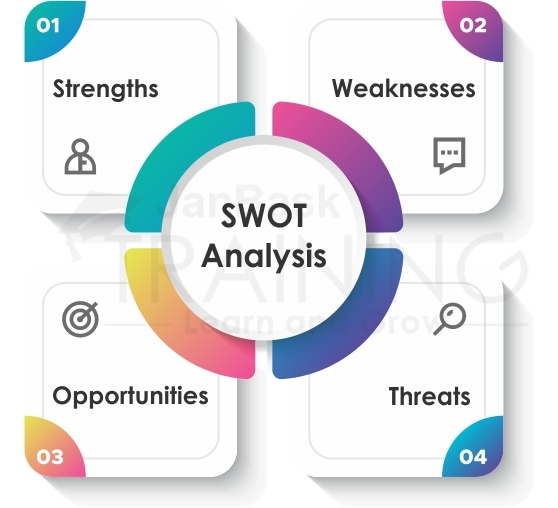
It is an elaborate analysis carried out by businesses on four parameters which if worked out will give rich information which can be used further in business processes. The first two, namely, the strengths and weaknesses refer to internal processes while the next two, namely, the opportunities and threats, refer to external processes.
Another powerful weapon in the hands of the business analysts for enhancing its strategy. It just helps businesses to set definite targets for the entire team and organization.
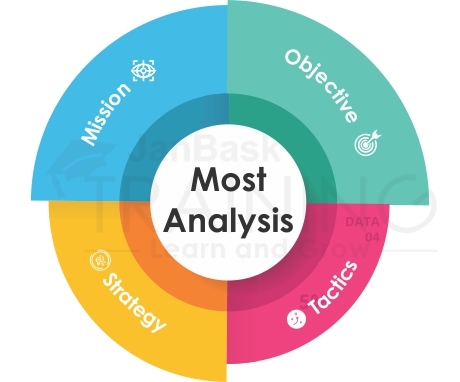
It has four elements:
This is usually undertaken to revitalize the look and appeal of the organization when it is looking to refine the purpose and mission.
It refers to a graphical representation of the business process of an organization or any particular workflow which has been defined. In this process, a line of suggestions are presented to the business owners for modifying their current model to make it more profitable and scalable. It is considered as a legacy process used during the analysis phase of development. The International Institute of Business Analysis conducts the following tasks under the BPM:
It is an easy choice for representation of a business process which is operated by different roles. It is one of the biggest analysis techniques which are employed by the industry, especially the IT industry. It helps the whole team to visualize the process of execution. It helps to make a more straightforward analysis.
Business Analyst Training & Certification

This technique is generally used when there is a change in the technical solution to a particular problem. The primary aim of the business analyst is ensuring system performance and requirements of data storage. This is done for measurement of the performance factors for live data. The NFR Analysis is taken up during the Analysis phase while it is implemented in the Design Phase. The non-functional requirements are as follows:
It is often carried out by the business analyst for capturing the requirements of the clients and the customers. It is these sessions which usually lead to valuable insights for the business and result in solving a complex problem. It is a group activity carried out for a generation of more ideas, root cause analysis, and even proposing solutions to various problems. It is the baseline technology which works for other business analysis techniques as well as the SWOT analysis, Most analysis, etc.
This is again a vital part of the product lifecycle, which is started when the stakeholders usually come up with a solution. Here in a business analyst is required to undertake many interviews for understanding the basic intention of requirements. It is not possible for a project to carry out the right development without a proper requirement analysis. Some of the components of these interviews are:
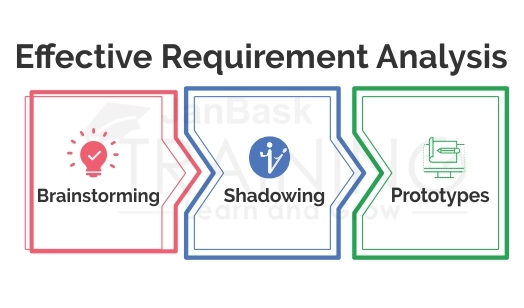
In addition to interviews, BA can also resort to the following techniques for an effective requirement analysis:
It stands for a generic thought process for business analysis for the understanding of the aim of business. It enumerates the pain points and how will the proposed solution impact both the business and its associated people. It is useful for bringing the perception of various stakeholders on common ground. A business analyst is thus left in a better position to prioritize different business perspectives based on their merits. CATWOE is basically an acronym which stands for:
Clients, Actors, Transformation, World View, Owner, and Environmental Constraints
This is seen as a modern technique of business analysis primarily used in the agile model. In the latter, there is an increased need for iterations for the gathering of requirements, designing and building a project. Requirements are collected from the users to build the best of their solutions. As this involves the user perspective as the central idea, so this is highly effective.
Environmental factors have profound and obvious impacts on the businesses and have to be factored in during any kind of strategic planning.

The main factors which are involved as known as PESTLE, referring to:
Business Analyst Training & Certification

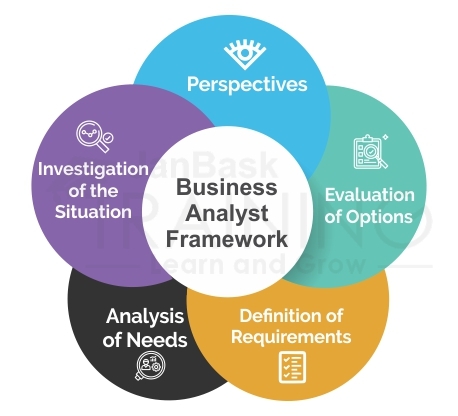
The whole business analysis framework is divided into five sections. In each of this section, a business analyst identifies, analyses and makes a note of all the requirements. There are many subtasks associated with each of these sections, which will, in return, help the business analyst to document the same requirements from different business owners and stakeholders.
Business Analyst Training & Certification

The main purpose of the business analysis framework is to make sure that all the business processes are streamlined and carried out with ease. It also reflects on all the techniques which can be used by business analysts for the gathering of requirements and for carrying out different aspects of analysis. A good business analyst always adheres to the fundamentals of the basic framework. His role is basically to make the client and the customer happy by ensuring their requirements have been met. The whole process works fine is the prime responsibility of the analyst.
At Janbask Training, we try to cover all aspects of the business analyst profile to make you job-ready. You may visit the website for more information about our courses.
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Interviews