15
JulInternational Womens Day : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
In the vast era of information technology, web, mobile, gaming, and Internet of Things are the top trends that are popular among the modern generation. Amazon’s DynamoDB is the top database solution among cloud computing environment. All the applications that need low-latency data access, DynamoDb is the solution. In this blog post, we will learn the fundamentals of DynamoDB, it's working, and a few of the fundamental concepts.
You can access Amazon DynamoDB by using three different methods: -
These are some of the key features of Amazon RDS. However, if you're preparing to sit for your Cloud Computing certification? We recommend you to go through various AWS blogs available on the JanBask Training that has been curated to help you become Industry-ready!
DynamoAPI offers a wide set of actions that require permissions. To set permissions, you have to establish the actions permitted, resources permitted, and conditions of each.
For example − dynamodb:CreateTable
You can also employ condition keys to filter permissions.
| API Operation | Necessary Permission |
| BatchGetItem | dynamodb:BatchGetItem |
| BatchWriteItem | dynamodb:BatchWriteItem |
| CreateTable | dynamodb:CreateTable |
| DeleteItem | dynamodb:DeleteItem |
| DeleteTable | dynamodb:DeleteTable |
| DescribeLimits | dynamodb:DescribeLimits |
| DescribeReservedCapacity | dynamodb:DescribeReservedCapacity |
| DescribeReservedCapacityOfferings | dynamodb:DescribeReservedCapacityOfferings |
| DescribeStream | dynamodb:DescribeStream |
| DescribeTable | dynamodb:DescribeTable |
| GetItem | dynamodb:GetItem |
| GetRecords | dynamodb:GetRecords |
| GetShardIterator | dynamodb:GetShardIterator |
| ListStreams | dynamodb:ListStreams |
| ListTables | dynamodb:ListTables |
| PurchaseReservedCapacityOfferings | dynamodb:PurchaseReservedCapacityOfferings |
| PutItem | dynamodb:PutItem |
| Query | dynamodb:Query |
| Scan | dynamodb:Scan |
| UpdateItem | dynamodb:UpdateItem |
| UpdateTable | dynamodb:UpdateTable |
Note: AWS is a big domain with multiple job roles. If you are a beginner looking to excel in your career in AWS. Check out the best High-Paying Cloud Certifications in 2022 that can remarkably boost your career.
In the following table, you can view the resources associated with each permitted API action −
| API Operation | Resource |
| BatchGetItem | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| BatchWriteItem | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| CreateTable | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| DeleteItem | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| DeleteTable | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| DescribeLimits | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:* |
| DescribeReservedCapacity | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:* |
| DescribeReservedCapacityOfferings | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:* |
| DescribeStream | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name/stream/stream-label |
| DescribeTable | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| GetItem | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| GetRecords | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name/stream/stream-label |
| GetShardIterator | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name/stream/stream-label |
| ListStreams | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name/stream/* |
| ListTables | * |
| PurchaseReservedCapacityOfferings | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:* |
| PutItem | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| Query | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name/index/index-name |
| Scan | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name/index/index-name |
| UpdateItem | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
| UpdateTable | arn:aws:dynamodb:region:account-id:table/table-name |
As an instance, the classification of DynamoDB is as follows: -
Tip: Amazon Web Services is the hottest cloud computing infrastructure with a hyper-scale market share of 49 percent. If you want to know which AWS Jobs are trending check out the AWS Developer Salary Guide, get real numbers & choose the right career
You can install a downloadable version of Amazon DynamoDB into your system which is provided in an executable .jar file. The downloaded file can be installed and run on Windows, Linux, MacOS, and the systems that run on Java.
You need to have Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 6.x or above installed on your system. The application does not run on earlier versions of JRE.
Following steps will allow you to set up and run DynamoDB on your computer system: -
DynamoDBLocal.jar, and enter the following command. java -Djava.library.path=./DynamoDBLocal_lib -jar DynamoDBLocal.jar -sharedDbjava -D"java.library.path=./DynamoDBLocal_lib" -jar DynamoDBLocal.jarDynamoDB processes incoming requests until you stop it. To stop DynamoDB, press Ctrl+C at the command prompt. DynamoDB uses port 8000 by default. If port 8000 is unavailable, this command throws an exception. For a complete list of DynamoDB runtime options, including -port, enter this command. java -Djava.library.path=./DynamoDBLocal_lib -jar DynamoDBLocal.jar -helpAWS Access Key ID: "fakeMyKeyId" AWS Secret Access Key: "fakeSecretAccessKey" You can use the aws configure command of the AWS CLI to set up credentials.aws dynamodb list-tables --endpoint-url http://localhost:8000Now, if cloud computing fascinates you and you want to make a long-term career around it, more specifically in AWS technology then check out the AWS Career Path and gain a complete insight about this most demanded IT profession.
If you plan to interact with DynamoDB only through the AWS Management Console, you don't need an AWS access key, and you can skip ahead to Using the Console.
To use the Amazon DynamoDB web services, you need to perform the following steps: -
To use the DynamoDB service, you must have an AWS account. If you don't already have an account, you are prompted to create one when you sign up. You're not charged for any AWS services that you sign up for unless you use them.
Part of the sign-up procedure involves receiving a phone call and entering a verification code on the phone keypad.
Before you can access DynamoDB programmatically or through the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), you must have an AWS access key. You don't need an access key if you plan to use the DynamoDB console only.
Access keys consist of an access key ID and secret access key, which are used to sign programmatic requests that you make to AWS. If you don't have access keys, you can create them from the AWS Management Console. As a best practice, do not use the AWS account root user access keys for any task where it's not required. Instead, create a new administrator IAM user with access keys for yourself.
The only time that you can view or download the secret access key is when you create the keys. You cannot recover them later. However, you can create new access keys at any time. You must also have permission to perform the required IAM actions.
However, to stay current with the change in the cloud computing environment, students and professionals should follow some of the top AWS thought leaders and influencers. Check out this comprehensive list of industry Best AWS Influencers/Leaders you must follow!
AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLEwJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEYBefore you can access DynamoDB programmatically or through the AWS CLI, you should configure your credentials to enable authorization for your applications.
There are several ways to do this. For example, you can manually create the credentials file to store your access key ID and secret access key. You also can use the AWS configure command of the AWS CLI to create the file automatically. Alternatively, you can use environment variables.Before moving to the next section, let’s quickly go through the Free AWS Quiz to practice what you have learned so far.
The following diagram shows a table named People with some example items and attributes-

Note the following about the People table:
Note: Comprehensive knowledge of Amazon DynamoDB can make you a superstar in AWS so can knowledge of Amazon Migration. Hence, If you are looking to make your career in AWS and land a high-paying job, consider enrolling in a professional Cloud Migration Course.
When you create a table, in addition to the table name, you have to specify the primary key of the table. The primary key uniquely identifies each item in the table, so that no two items can have the same key.
DynamoDB supports two different kinds of primary keys:
You can create one or more secondary indexes on a table. A secondary index lets you query the data in the table using an alternate key, in addition to queries against the primary key. DynamoDB doesn't require that you use indexes, but they give your applications more flexibility when querying your data. After you create a secondary index on a table, you can read data from the index in much the same way as you do from the table.
DynamoDB supports two kinds of indexes:
Each table in DynamoDB has a limit of 20 global secondary indexes (default limit) and five local secondary indexes per table.
Also, if you want to enhance your knowledge of AWS. Check out the AWS Step Functions Concepts with Example to gain complete insight o this domain. Next, we will check through the Amazon DynamoDB Streams.
DynamoDB Streams is an optional feature that captures data modification events in DynamoDB tables. The data about these events appear in the stream in near-real-time, and in the order that the events occurred.
Each stream record also contains the name of the table, the event timestamp, and other metadata. Stream records have a lifetime of 24 hours; after that, they are automatically removed from the stream.
You can use DynamoDB Streams together with AWS Lambda to create a trigger—code that executes automatically whenever an event of interest appears in a stream. For example, consider a Customers table that contains customer information for a company. Assume that you want to send a "welcome" email to each new customer. You can allow a stream on that table, and then associate the stream with a Lambda function. The Lambda function will execute whenever a new stream record appears, but only process new items added to the Customers table. For any item that has an EmailAddress attribute, the Lambda function would invoke Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) to send an email to that address.

In the above example, the last customer, Craig Roe, will not receive an email because he doesn't have an Email Address. However, if you are a beginner and want to know how to create your own first amazon ec2 instance and gain in-depth knowledge on What Is AWS Lambda? We recommend you check out these blogs.
A DynamoDB database can be broken down into three theorems:

A DynamoDB table must have a primary key. There are two possible types to choose from:
Your DynamoDB partition key must be unique and sparse. As this key is hashed internally and used to distribute that data for storage. This is a similar technique to Redshift and HBase that prevents hot-spotting of data.
If using a composite key, then two items can have the same Partition Key, but the Sort Key must be unique. This will mean all items with the same Partition key will be stored together but sorted in ascending order using the Sort Key.
Tip: AWS is a big domain with multiple career options. Yet, for the maximum impact learning, AWS from scratch is important, check out our complete AWS Training & Certification Guide for a rewarding career ahead.
Step 1: Navigate to the DynamoDB section in AWS. Select “Create Table“.

Step 2: Fill in with the necessary details and click on “Create.“

Step 3: You can view your table being created. Click on “Overview” to understand your table, click on “Items” to edit, insert and query on the table. There are many more options you can use to understand your table better.

Step 1: Navigate to the DynamoDB section in AWS. Select “Create Table“.

Step 2: Fill in with the necessary details and click on “Create.“

Step 3: You can view your table being created. Click on “Overview” to understand your table, click on “Items” to edit, insert and query on the table. There are many more options you can use to understand your table better.

Step 1: Navigate to “Items” and click on “Create item.“

Step 2: It will open a JSON file where you can add different items. Click on the “+” symbol and select “Append” and select what type of data you want to enter.

Step 3: This is what it looks like after adding multiple columns to your table. Click on “Save“.

Step 4: Since it is a NoSQL architecture, you can play around with the columns you add to the table. E.g., “Position.“
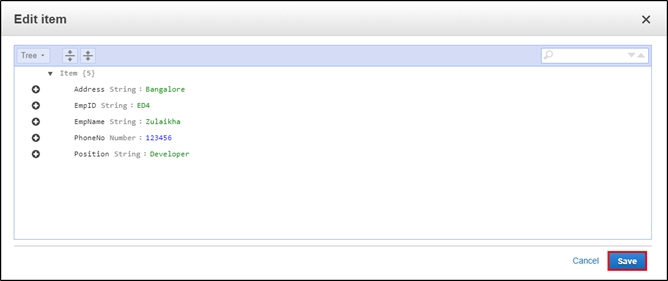
Step 5: This is how your table will look like once you have inserted the data.

Further, if you are looking to garner more information, check out our blog on why EC2 in AWS is the Backbone of AWS to gain better insight.
Step 1: Here, you can frame your query and click on “Start Search” to get the desired result.
E.g., I am searching for all the mobile numbers that are greater than or equals to “1234“.
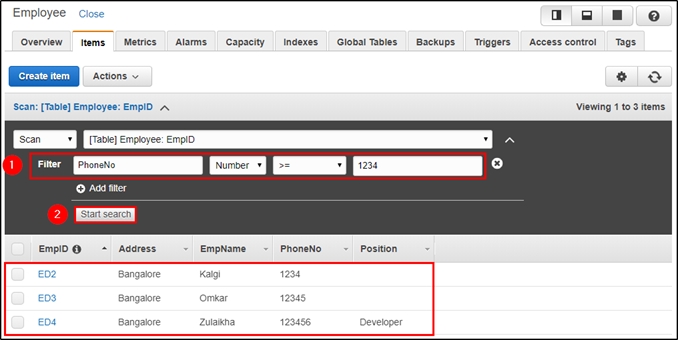
Step 2: Here, I am searching for the record which has EmpId as “ED4“.

The above steps will allow you to create, insert, and query a table in DynamoDB. Consider enrolling in an AWS Training Course to get better insights into AWS and other platforms.
So, gear up and give a jumpstart to your AWS professional career by enrolling yourself in a comprehensive AWS Certification Course, today! If you have any questions for us? Feel free to ask or talk to our counselor; we’ll get back to you! Also, don’t forget to join the professional JanBask AWS Community to get professional guidance and the best career advice.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
AWS vs. OpenStack vs. SoftLayer - Which One is the Best?
![]() 235.1k
235.1k
EC2 in AWS - The Backbone of AWS
![]() 5.8k
5.8k
Amazon Redshift vs Amazon RDS vs DynamoDB vs SimpleDB
![]() 15.6k
15.6k
Difference between AWS Inspector and AWS Trusted Advisor
![]() 833.4k
833.4k
AWS Certified Developer Associate Certification Guide: Exam Format, Cost & Exam Tips
![]() 220.6k
220.6k
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on AWS Course
Interviews