Introduction
Lot of people outside of the information security or Cybersecurity community think of the CIA as people in suits and ties, just like an intelligence agent or undercover agent. But this acronym also epitomizes Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability in Cybersecurity, which helps protect businesses from vulnerabilities. Simply put, by strengthening the security policies, the CIA triad can perform everything to keep your business’s data, networks, and systems safe and secure.
For the smooth operations of any business, confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information are necessary. The CIA triad splits these 3 pillars into important points, which help security teams set security measures. Ideally, when these 3 standards come together, your business's security posture strengthens and becomes fully equipped to safeguard from threats.
Everyone currently working or enthusiastic about learning Cybersecurity online or infosec needs in-depth knowledge of the CIA triad, and this blog will definitely help you.
What Does the CIA Triad Stand for in Cyber Security?
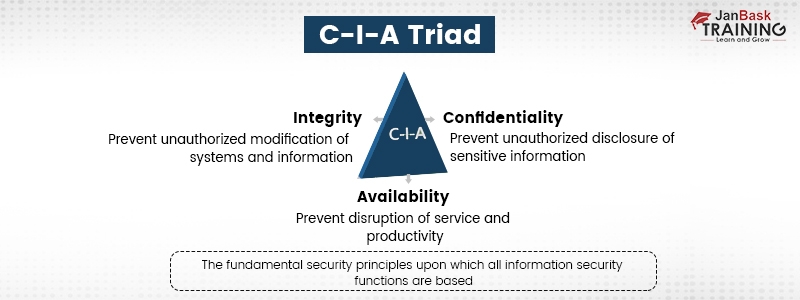
It stands for Confidentiality, integrity, and availability, an all-inclusive infosecurity model. It helps an organization’s security measures to assure data security. These 3 pillars help form the basis of a security posture. No doubt, applying these standards to any security program is beneficial.
- Confidentiality - Assures that only an authorized person has access or permission to alter the data.
- Integrity - Helps in managing data's legitimacy by embracing it properly and being resistant to any type of incorrect changes.
- Availability - Any legitimate user can access the data whenever needed.

The CIA model or CIA triangle is very fundamental to data security. Whenever any data violation or security incident occurs, it’s surely due to one or more of these CIA triads being hampered. So, the CIA model is always the high priority for any infosecurity expert. Understand the difference between information security and Cybersecurity by clicking here.
Infosec professionals evaluate threats and vulnerabilities, inspecting the effect that they might have on the CIA model of your business’s resources. Based on that analysis, the security team enforces a particular set of security policies to minimize the risks inside that environment.
Break Down of 3 Key Concepts in the CIA triad
In this section, we’ll get you through a precise and in-depth explanation of these key concepts related to infosecurity and what the CIA stands for in information security.
Confidentiality
involves a business's attempts to ensure that the data is protected. To accomplish this, one should administer the permissions to access information and prevent unauthorized data sharing, whether intentionally or accidentally. The central idea for keeping up with confidentiality is ensuring that persons without legal authority must be restricted from accessing confidential business elements.
On the other hand, an effective system assures those who need access must have the required permissions. For example, those who work in finance departments must also be capable of accessing spreadsheets, bank account records, and other information related to finance. But despite that, a larger number of other staff, including a few executives, should not get access. Tight restrictions must be in place to ensure these policies are adequately followed.
Confidentiality could be compromised in a number of ways, together with direct attacks trying to get unauthorized access to the devices. Here, a cyber attacker can directly try to invade a database or an application to access or change sensitive data.
The cyber attackers could use various techniques such as MITM (Man-in-the-Middle) attacks, where the attacker interweaves themselves in the middle of a conversation to steal or modify confidential data. Few cyber attackers try to gain unauthorized access to credentials with the help of different ways of network spying.
In some cases, the attackers might try to gain access to more than one privilege to attain the next level of precision.
In spite of that, not all confidentiality breaches are intentional. Human errors or inappropriate security measures can be responsible as well. For instance, somebody might fall short of securing the password due to logging into a restricted area. At times a user might not encrypt the communication properly, facilitating an attacker to steal important data.
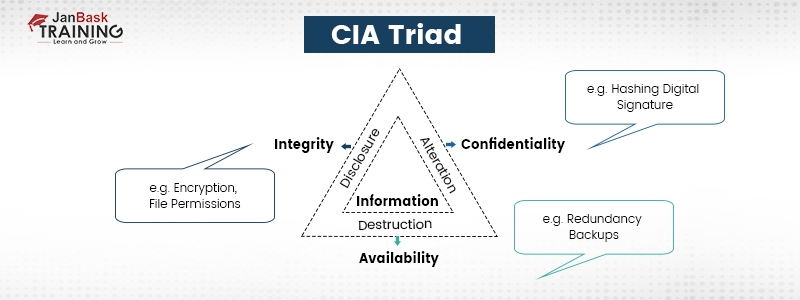
To avoid confidentiality breaches, you need to classify and label the restricted data, deploy access control policies, encrypt data, and make use of MFA systems. Also, everyone in the organization should have adequate knowledge and training to find out the security threats and avoid them. As a Cybersecurity professional, it's important to have a knowledge of different types of Cybersecurity attacks.
Integrity
Makes sure that your data is authentic and devoid of any tampering. Data integrity can be maintained provided the data is worthwhile, precise, and trustable. For instance, if your organization gives information about administrators on your company website, then that information requires to have integrity. And if the information is inaccurate, the visitors might feel that your company is unreliable.
Also, any attacker with an equitable interest in harming your organization’s reputation might try to manipulate your website and edit the information like descriptions, images, or titles of administrators to damage their reputation or your organization.

Integrity is often compromised intentionally. A hacker might circumvent the IDS (Intrusion Detection System), alter the file configuration to approve unauthorized access, or modify logs stored by the system to mask the attack. Integrity can also be infringed accidentally. Anyone can accidentally add the wrong code or make any irresponsible error. Also, remember that not all hackers are criminals; few are employed to foil illegal activity. They’re known as ethical hackers. Learn more about ethical hacking, its types, and career options here.
If the organization’s security measures and procedures are insufficient, integrity might get violated without just one person in the organization answerable for the mistake. To safeguard data integrity, make use of hashing, encryption, digital signatures, and certificates. For your business website, you must install an SSL certificate so visitors can trust your website. Non-repudiation can be used to verify data integrity when something can’t be rejected or prohibited. For instance, if your employees use digital signatures while sending emails, the email coming from them can’t be blocked.
A method used for authenticating integrity is non-repudiation, i.e. when something can’t be declined. For instance, if staff members in your organization use digital signatures while sending emails, the truth is that their email can’t be declined. Also, the recipient can’t decline that they’ve received an email from the respective sender.
Availability
Even though the data is held confidential and its integrity is managed, it's usually in vain unless and until it is made available to required persons in the organization and to the customers to whom they provide service. It implies that systems, networks, applications, etc., must function as they need to be and when they should be. Additionally, persons with access to certain information should be capable of consuming that information whenever necessary, and fetching the data must not require a long time.
For instance, if there’s a power outage and also if there’s no disaster recovery system in place to assist end users in getting back access to important systems, availability will get hampered. As well as, a natural calamity such as a flood or an extreme hailstorm might prevent end users from reaching the office, which can disturb the availability of their workplaces, and other systems can offer mission-critical information or applications. Availability can also get compromised due to intentional acts of destruction like DDoS (Distributed-Denial-of-Service) attacks or ransomware attacks.
Companies can use redundant networks, servers, and applications to ascertain availability. These can be planned to become accessible when the original system gets broken or disrupted. You can also improve availability by staying abreast of upgrades to software applications and security measures. This will help prevent applications from getting malfunctioning or preventing new threats from infiltrating your system. Immediately after any negative event, backups and complete disaster recovery plans also help businesses to regain availability.
CIA Triad Examples to Better Understand How it Works
To understand better what the CIA stands for in information security or how it works, assume an ATM that facilitates end users to check their bank balance and other required information. An ATM integrates ways to cover three principle standards of a CIA triad -
- The 2FA (2-factor authentication), i.e., a debit card with a PIN, offers confidentiality prior to authorizing access to confidential information.
- The ATM and bank application assure data integrity by managing all transfer and withdrawal records done through the ATM in the end user’s current accounts.
- The ATM also provides availability since it’s for public use and is accessible anytime.
Do you wish to get one step closer to Cybersecurity? Read this blog and deep dive into the world of cyber security.
History of the CIA Triad
The conception of the CIA security triad is structured over time and doesn’t have any creator. Confidentiality might have been first proposed as early as 1976 in a study by the U.S. Air Force. Similarly, integrity was invented in a paper titled - A Comparison of Commercial and Military Computer Security Policies - in 1987, written by David Clark and David Wilson.
The paper discovered that commercial computing needed accounting financial records and data accuracy. Even if it isn’t as easy to identify original source, the concept of availability became more comprehensive a year later, i.e., in 1988. By 1998, people saw the three principle concepts as a CIA triad.
Importance of the CIA Model
What the CIA triad stands for? And what is the importance of the CIA model? The CIA triad imparts an extraordinary all-inclusive checklist for determining your security measures and tools. A compelling system like the one we just discussed under the section CIA triad example fulfills all three principles - confidentiality, integrity, and availability. An infosec system devoid of one of the three CIA triad in information security is incomplete.
This triad is also useful for analyzing what has gone wrong or what worked as desired after any negative event. For instance, possibly, availability gets compromised after a cyberattack like ransomware. Still, the systems in place might be able to manage the confidentiality of crucial information. This data can be used to address weak points and recreate effective policies and deployments.
Best practices for implementing CIA triads
It's not sufficient to know about the CIA security triad, but one should understand its precedence on different elements to implement appropriately. Different elements can include the organization’s security goals, type of business, industry, and relevant governing needs.
Take, for example, a government intelligence agency. Undoubtedly, confidentiality is more important in these types of organizations. On the contrary, integrity is crucial in a financial organization as precise accounting of transactions and balances could avoid harmful damages. Even so, for healthcare and eCommerce organizations, availability is preferred to avoid downtime or demise.
It's also necessary to remember that emphasizing one or more CIA triads in information security principles can affect others. For example, any system that needs higher confidentiality and integrity may need to forgo speedy performance that other systems may prefer or need more. This bargaining is certainly not bad as the decisions are taken cautiously with professionalism. Hence, each business should consider implementing the CIA triad in information security, depending on personal needs.
When should you use the CIA triad in Cybersecurity?
In most security incidences, CIA triads should be used because every element is crucial. Despite that, it's primarily useful when building systems around data classification and handling permissions and access rights. It's important to precisely implement the CIA information security triad while managing the vulnerabilities of your business. It could be used as a powerful tool for disrupting the Cyber Kill Chain or attack chain, which indicates a course of targeting and executing a cyberattack.
The CIA triad in Cybersecurity can also help you zero in on what cyber attackers might be after and then implement strategies and tools to secure those resources appropriately. Furthermore, this triad could be used when training employees about cybersecurity. Hypothetical plots or real-life case studies can help employees envision the management of confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and systems.
Understanding what the CIA stands for in Cyber Security. But to explore more than this, enroll in online CISSP training and certification course now.
Cybersecurity: A new frontier in the IT sector
Even though the major goal of Cybersecurity is securing networks, applications, and data from attackers, unauthorized access, or any kind of damage, this sector is formed by advanced technologies, processes, and best practices. Other terms used to refer to it includes- Information Technology Security or IT Security since information technology departments are responsible for security and defense.
Therefore, Cybersecurity is crucial for all domains - from Government agencies to Corporate offices, military to healthcare centers, and financial to personal security. Because each of these domains is required to gather, store, retrieve and transfer the data, most of which is confidential.
As digital information and transactions increase, so does the requirement for cyber security experts in different roles. Which has opened the doors to successful careers! There are several compelling reasons to be a cyber security certified professional or to change or advance in your existing career, like - solid demand in the job market, salary, opportunities, etc.
Conclusion
The CIA triad serves as a beneficial criterion that accounts for the need for security measures. All the security policies automatically get traced back to one or more than one of the three CIA principles. Hence it's important to understand the CIA triad. A possibility is that you might have observed that - the central theme of the CIA triad is “Information”. When it is viewed as a central point of most infosecurity, it offers a restricted view of security, which overlooks other crucial factors.
For instance, although the availability may guarantee you won’t lose access to assets required to give information whenever required, considering information security by itself doesn’t ensure that a different person has not used your hardware parts without permission. Hence understanding what the CIA triad is and how it can be used to strategize and also achieve better security policy while at the same time understanding the different principles behind it is beneficial. Get in touch with our experts at JanBask Training to learn more about CyberSecurity courses online.
FAQS
Q1. Give an Overview of Your Cybersecurity Training & Certification Course.
Ans:- Our CyberSecurity training and certification program will help candidates learn the skills to become experts in this rapidly flourishing industry. Candidates will learn all-inclusive methods to protect business infrastructure, secure data and information, perform risk analysis and mitigation, architect cloud-based security, achieve compliance, and much more.
Q2. Is Cybersecurity a Promising Career?
Ans:- The Cybersecurity sector has more employment opportunities than the no. of qualified professionals to fill them. There are more than half a million Cybersecurity job openings in the US. these are all well-paid jobs, and according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics report, the average salary of an information security analyst in the U.S. is $102,600.
Q3. What Skills are Required for Learning Cybersecurity?
Ans:- As a Cybersecurity professional, the skills, practices, and technologies you’ll use will evolve continuously with computer and network technologies. The curiosity to learn, problem-solving ability, attentiveness, etc., will benefit you in this sector. But other critical technical skills and technologies you must learn include -
- SIEM tools, i.e., Security Information and Event Management
- Firewalls, Intrusion Detection Systems, and Intrusion Prevention Systems
- Digital forensics
- Mobile device management
- Data management
- Application security development
- Audit and compliance knowledge
Q4. What Human Skills are Needed for Cybersecurity?
Ans:- Human skills often required in efficient cybersecurity professionals include communication, collaboration, risk management, adaptability, and critical thinking.
Q5. Dose Cybersecurity Require Coding Knowledge?
Ans:- Most entry-level cybersecurity jobs don’t require coding skills, but they are essential for mid and senior-level cybersecurity jobs.
Q6. Which Cybersecurity Certification Should a Beginner As I Get?
Ans:- If you’re just beginning in Cybersecurity, consider doing CISSP certification, which will help you build fundamental Cybersecurity skills and get hands-on experience with different tools. Once you establish familiarity with Cybersecurity technologies and best practices, the CEH certification will also be helpful to you.
Q7. How Long does it Take to Get Cybersecurity Certification?
Ans:- The duration will depend on what you already know and what you need to learn. Preparation could take anywhere from a week to a few months.
Q8. Does Cybersecurity Need a lot of Math?
Ans:- Cybersecurity doesn’t require a lot of math since it's considered a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) concentration, and math knowledge will help you move forward in your career.
Security professionals often need to calculate risks, which requires math, and statistics, including logic. Also when understanding and writing programming codes requires having a fundamental knowledge of math.
At last, cryptography in Cybersecurity is a science of codes and encryption, and it requires a knowledge of mathematics to decipher and develop algorithms for automatized reasoning and data processing.
Q9. Who should Enroll in Your Cybersecurity Master Training and Certification Program?
Ans:- Our Cybersecurity master’s training and certification program are best suited for
- All levels of IT auditor or penetration tester
- Security consultants or managers
- IT directors or managers or consultants
- Security auditors or architects
- Security systems engineers
- Chief information security officers (CISOs)
- Chief compliance or privacy or risk officers
- Network specialists, analysts, managers, architects, consultants or administrators
- Technical support engineers
- Systems analysts or administrators
Q10. What are the Prerequisites for Doing this Cybersecurity Training and Certification Program?
Ans:- Candidates need to have an undergraduate degree or a high school diploma.
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
1 day 19 Sep 2025
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
4 days 22 Sep 2025
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
1 day 19 Sep 2025
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
1 day 19 Sep 2025
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
1 day 19 Sep 2025
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
8 days 26 Sep 2025
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
7 days 25 Sep 2025
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
8 days 26 Sep 2025
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
2 days 20 Sep 2025
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
16 days 04 Oct 2025
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
29 days 17 Oct 2025
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
8 days 26 Sep 2025