24
JulGrab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Amazon RDS is the Relational Database Service offered as a web administration by Amazon. It makes it simple to set up and works as a social database in the cloud. It gives a very practical approach to utilizing the industry's driving RDBMS programming as a management service. Due to this web service from amazon AWS, you don't need to purchase any server or introduce any database software to it. You simply have to install the AWS RDS web server and begin utilizing the RDBMS addons after some underlying arrangement including memory and CPU limit distribution and other ancillary settings. This blog will introduce you to the concept of Amazon RDS. If you wish to get an in-depth understanding of the AWS platform and look for a bright career here, consider enrolling in the best AWS Training Course.
Amazon Relational Database is a management database administration that oversees, scales, and prepares the Relational Database to deal with the cloud. The client can browse MySQL, and Amazon Engine. The AWS additionally fixes the servers. AWS RDS gives the facility the end goal that the client has no compelling reason to rack and stack. Also, there is no compelling reason to introduce the product. The industry can rely upon Amazon RDS and focus on the integration of the organization as it analyses the client and set the database as indicated by it. It is easy to give high versatility to the data with Amazon RDS.
The AWS RDS is additionally secure towards a disaster as they have various storage centers located over the globe with the end goal that if one is destroyed for some reason, the other is as yet solid to continue the operations. The information is duplicated in the native environment or some faraway environment, and the procedure is done within a couple of snaps. Amazon RDS gives the benefit of the snapshot which a client can keep for giving the updated and upgraded security highlight to the data. However, to be a reputed AWS professional much depends on the certification you hold, consider going for industry-recognized Cloud computing certifications.
Amazon RDS has got the following features –

These are some of the key features of Amazon RDS. However, if you're preparing to sit for your Cloud Computing certification? We recommend you to go through various AWS blogs available on the JanBask Training that has been curated to help you become Industry-ready!
Step 1- Login to AWS the board comfort. Utilize the accompanying connect to open Amazon RDS comfort − https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
Step 2 − Select the area where the DB occasion is to be made, at the upper right corner of the Amazon RDS comfort.
Step 3 − Select Instances in the route sheet, at that point, click on the Launch DB Instance tab
Step 4 − The Launch DB Instance Wizard opens. Select the sort of example that is required to dispatch and tap on the Select tab.
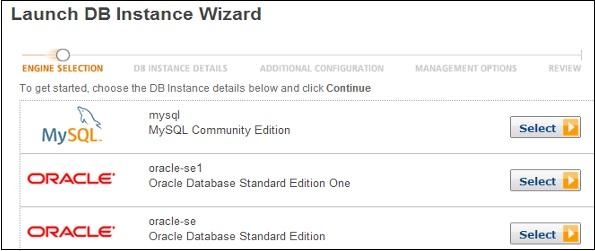
Step 5 − On the Specify DB Details page, give the required subtleties, and snap the Continue catch.

Step 6 − On the Additional design page, give the extra data required to dispatch the MySQL DB case and snap the Continue tab.

Step 7 − On Management alternatives page, settle on the decisions and snap the Continue tab.
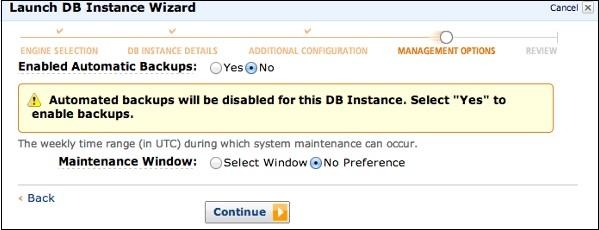
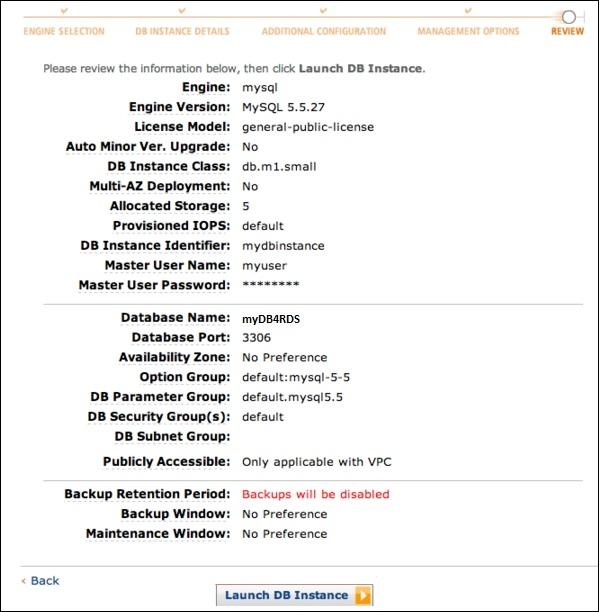
Step 8 − So, this is the complete process to set up AWS RDS. Before we move to the next section, have a quick go through the Free AWS Quiz.
Why do you want a managed relational database service? For what reason do you need an oversaw social database administration? Since Amazon RDS takes over many of the troublesome or repetitive administration assignments of a relational database:
As you might have already witnessed AWS RD has changed the way organizations work and if you are a beginner who wants to start an AWS Career! Check out our AWS Career Path & gain complete insight of this domain.
The fundamental building block of Amazon RDS is the DB instance. A DB instance is a secluded database condition in the cloud. A DB instance can contain various client-made databases, and you can get to it by utilizing similar apparatuses and applications that you use with an independent database instance. You can make and alter a DB instance by utilizing the AWS Command Line Interface, the Amazon RDS API, or the AWS Management Console.
Every DB instance runs a DB motor. Amazon RDS at present backings the MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server DB engine. Every DB engine has its own bolstered highlights, and every form of a DB engine may incorporate explicit highlights. Also, every DB motor has a lot of parameters in a DB parameter cluster that control the conduct of the databases that it manages.
The calculation and memory limit of a DB instance is dictated by its DB instance class. You can choose the DB instance that best addresses your issues. If your needs change after some time, you can change DB instances.
DB instance storage comes in three sorts: Magnetic, General Purpose (SSD), and Provisioned IOPS (PIOPS). The contrast in execution qualities and cost, enabling you to tailor your capacity execution and cost to the necessities of your database. Every DB instance has least and highest storage necessities relying upon the capacity type and the database engine it underpins. It's essential to have the adequate capacity with the goal that your databases have the space to develop and that highlights for the DB engine to provide space to compose content or log entries.
You can run a DB instance on a virtual private cloud utilizing the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) administration. When you utilize a virtual private cloud, you have command over your virtual systems administration condition: you can choose your own IP address, make subnets, and design steering and access control records. The fundamental usefulness of Amazon RDS is similar to whether it is running in a VPC or not; Amazon RDS oversees reinforcements, programming fixing, programmed disappointment recognition, and recuperation. There is no extra expense to run your DB instance in a VPC.
Amazon RDS uses the Network Time Protocol (NTP) to coordinate the time on DB Instances.
Now, that you have got a taste of AWS and the opportunities it presents to professionals, Check out the Top Reasons Why Aws Training Certification Can Change Your Life in 2022.
Amazon cloud computing assets are housed in exceedingly accessible data center facilities in various territories of the world (for instance, North America, Europe, or Asia). Every data center location area is known as a region.
Every area contains numerous distinct areas called Availability Zones, or AZs. Every Availability Zone is designed to be secluded from disappointments in other Availability Zones, and to give reasonable, low-dormancy arrange a network to other Availability Zones in a similar locale. By propelling occurrences in discrete Availability Zones, you can shield your applications from the disappointment of a single location.
You can run your DB instance in a few Availability Zones, a choice called a Multi-AZ arrangement. When you select this choice, Amazon naturally arrangements and keeps up an auxiliary reserve DB instance in an alternate Availability Zone. Your essential DB instance is synchronously reproduced crosswise over Availability Zones to the auxiliary instance to give data redundancy, failover support, dispense with I/O solidifies, and limit inactivity spikes during framework backups.
A security gathering controls the entrance to a DB instance. It does as such by enabling access to IP address extents or Amazon EC2 cases that you indicate.
Amazon RDS utilizes DB security gatherings, VPC security gatherings, and EC2 security gatherings. In straightforward terms, a DB security gathering controls access to a DB instance that isn't in a VPC, a VPC security group controls access to a DB instance inside a VPC, and an Amazon EC2 security gathering controls access to an EC2 occasion and can be utilized with a DB instance.
However, if you are a beginner and want to know how to create your own first amazon ec2 instance and gain in-depth knowledge on What Is AWS Lambda? We recommend you check out these blogs.
There are a few different ways that you can follow the presentation and soundness of a DB instance. You can utilize the free Amazon CloudWatch administration to screen the exhibition and soundness of a DB instance; execution diagrams are appeared in the Amazon RDS reassure. You can buy into Amazon RDS instances to be advised when changes happen with a DB instance, DB snapshot, DB parameter gathering, or DB security group.
There are numerous ways that you can interact with Amazon RDS.
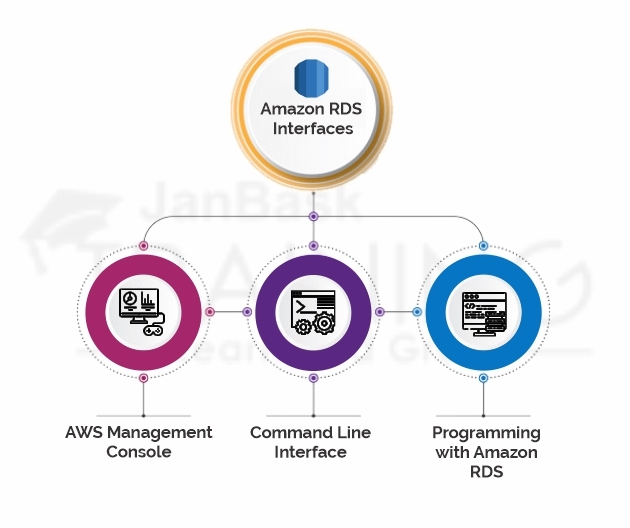
The AWS Management Console is a basic electronic UI. You can deal with your DB occurrences from the reassure with no programming required. To the Amazon RDS console, sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS support athttps://console.aws.amazon.com/rds
You can utilize the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) to get to the Amazon RDS API intuitively.
If you are a designer, you can access the Amazon RDS automatically.
For application improvement, we prescribe that you utilize one of the AWS Software Development Kits (SDKs). The AWS SDKs handle low-level subtleties, for example, verification, retry rationale, and mistake taking care of, with the goal that you can concentrate on your application rationale. AWS SDKs are accessible for a wide assortment of languages.
AWS additionally gives libraries, test code, instructional exercises, and different assets to enable you to begin all the more effectively.
However, If you are a beginner looking to excel in your career in AWS. Check out the best High-Paying Cloud Certifications in 2022 that can remarkably boost your career. Next, we will check through the Amazon RDS Basic Operational Guidelines.
The following are the fundamental operational rules that everybody ought to pursue when working with Amazon RDS. Note that the Amazon RDS Service Level Agreement necessitates that you pursue these rules:
When utilizing Amazon RDS, pay just for just the utilization with no minimum as well as arrangement charges. Charging depends on the accompanying criteria –

I hope you have gained some foundational knowledge about Amazon RDS. As said above, if you want to learn more about the AWS cloud, take an AWS Certification Course. If you have any doubts or queries, please leave them in the comments section of the blog. Also, don’t forget to join the professional JanBask AWS Community for the right career guidance and expert advice.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
AWS Object Storage and CDN (S3, Glacier and CloudFront)
![]() 4.7k
4.7k
Advance Your Technical Skills by Enrolling in Microsoft Azure Certification
![]() 124.3k
124.3k
Advantages And Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
![]() 787.9k
787.9k
Difference between AWS Inspector and AWS Trusted Advisor
![]() 833.4k
833.4k
What is AWS Lightsail? Amazon EC2 vs. Amazon Lightsail
![]() 656.2k
656.2k
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on AWS Course
Interviews