19
JulGrab Deal : Flat 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Containers have become one of the most important and imperative tools in the IT world. Today, most of the organizations use containers for deployment rather than using virtual machines. Now, we can describe what Kubernetes is. In this Kubernetes Tutorial, we will discuss what is Kubernetes and why it is being used along with the features of Kubernetes. However, Companies are also using Docker as a container tool. Even companies are using containers for deployment architecture and Kubernetes deployment is one such container that is used by most of the companies.
In this Kubernetes Tutorial, we will first discuss what is Kubernetes? Kubernetes is basically an open-source orchestration container management tool. The responsibilities of this tool include container deployment, scaling, and descaling of the container along with their load balancing. You may think that Kubernetes is an ordinary tool, but in reality, as Docker is necessary to create the containers so Kubernetes is important for managing them.
Today, most of the companies are using containers that may be either Docker, Rocket, or simple Linux containers to containerize the application, but they use it massively in 10’s or 100’s number, so may require load balancing just to ensure high availability and manage traffic. Even with the increased number of service requests the number of containers will also have to be increased by the organizations vice versa is also true, that means as the number of requests will be decreased the number of containers will also be minimized.
Practically it needs lots of manual effort in managing the containers. Automated management will make the task quite easier. This is what container management tools do. Docker, Swarm, and Kubernetes like tools are popular to manage the orchestration of containers. Being a Google brainchild Kubernetes is quite popular as a content management tool. Through Kubernetes, one can do automatic scaling as per traffic requirement.
Now as we have discussed so far about Kubernetes and what are they? Now is the time to discuss the features of Kubernetes. It offers the following organizational beneficial features:
Applications are automatically packaged and scheduled as per the availability and requirement of the resources even without sacrificing any user. To save unused resources and for complete utilization, Kubernetes balances best-effort and critical workloads.
Kubernetes automatically assign IP addresses to the containers and the set of containers are assigned a single DNS name, so users need not worry about communication and networking. It can even load balance the traffic inside the clusters.
You can mount the storage system of your choice with Kubernetes. For storage purposes, you can either use a public cloud provider like AWS or GCP or NFS, iSCSI like shared network storage system. So, the user is free to use any storage system of his choice with the help of Kubernetes.
Kubernetes can automatically start and restart those containers that could not start during execution and can kill those that do not respond to user-defined health checks. In case if a node dies they then either they are restarted or rescheduled on other available nodes.
Batch and CI workloads can also be managed by Kubernetes along with service management, so the containers that fail can also be replaced if required.
Read: The Truth About Jenkins Configuration Is About To Be Revealed
Just by a single command, Kubernetes can scale up the containers and to scale down you will also have to use only a single command. Kubernetes dashboard can also be used to scale up and down the system.
Kubernetes can automatically update and configure the applications in a progressive manner by ensuring that all instances will work in the same instance. Kubernetes can also rollback the changes done by the user if something goes wrong.
These are a few of the considerable features of Kubernetes. Even users can avail of any other features of Kubernetes by using it as a container management tool.
DevOps Training & Certification Course

Now, we are going to explore the architecture in this Kubernetes Tutorial. The architecture of Kubernetes is the ultimate reason for its amazing performance. All functioning that is involved in Kubernetes is all because of the architecture and working mechanism of the tool itself.

Kubernetes follows cluster computing architecture so everything or device is treated as a cluster or Kubernetes cluster, that is hosted by one node that is ultimately master of the cluster, while other nodes are known as nodes, that actually perform containerization.
In the Kubernetes master cluster or node controls the nodes. The master cluster ensures node execution and coordinates the complete process. The nodes are grouped together logically and are called Pods. Multiple Pods can be run by each node, which is a group of containers that interact with each other for deployment purposes.
It is a collection of four processes that run on a single node that is present in your cluster and is known as the master node.
Read: Know Everything About DevOps Engineer & Architect Salary
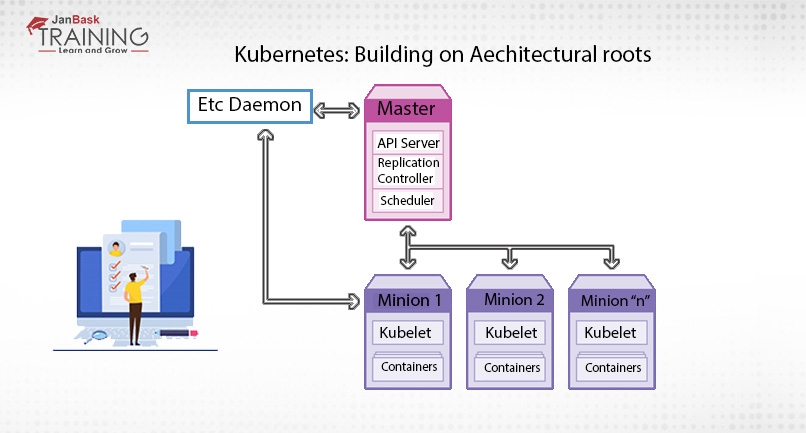
The four processes that run on the master node are:
This process is basically the brain of the master or control plane. It consumes JSON via a manifest file and implements RESTful API. The manifest file declares the app state and validates and deploys it on the cluster. An endpoint is exposed on port 443 so that Kubel can issue queries and commands that run on the master cluster node.
Cluster store is stateful and provides persistent storage by using etcd. Here etcd is an open-source key-value distribution store that is considered as the backbone of the distributed systems. They provide them with a useful and canonical hub with which they can manage cluster state and coordinate their functioning. Data storage and replication are being handled by etcd for the entire cluster.
It is a daemon process and controller of other controllers. The shared cluster state is watched by it through the API server and switching of cluster states also maintained by it. Some of the commonly used containers of Kubernetes are endpoints controller, replication controller, service account controller and namespace controller.
As per requirement, the controller implements the procedures that fulfill the desired state. The states may be scaling up and down or point adjustment. Pod template is provided for the replication controller.
This process just watches API-server for new pods and assigns workloads to any specific cluster node. On each host, resource utilization is also ensured and managed by it. Moreover, its major responsibility is to make sure that the workload will be distributed as per resource availability.
DevOps Training & Certification Course

Those servers that do actual work are called nodes. Each Kubernete cluster runs two processes:
Read: Azure DevOps Engineer Salary: Everything You Need to Know
It is the main agent of the Kubernetes that is a registered node within the cluster. For the work assignment, you can watch the API server and instantiate pods to carry out the work. Nodes report back to the master and the endpoints are exposed on port-10255.
Kube proxy is the heart of the network proxy of Kubernetes that reflects Kubernetes networking services on each node. It provides a unique IP to every pod. The same IP will be shared by multiple containers. Load balancing is also done by Kube-proxy.
The Pod is the basic building block and a single unit of Kubernetes. The containers are run in this ring-paced environment. Usually, a single container is being run inside a pod, in tightly coupled systems two containers in a pod. Through an overlay, network pods get connected to the rest of the environment. Each pod has a unique IT address and namespace, including IP address and network port, is shared by every pod.
Pods of Kubernetes are mortal and after death can’t be resurrected. So, when a pod is crashed down a new pod is being added with a unique but different IP address. Due to this pod discovery becomes difficult as it is difficult to know which pod gets added and deleted. Through services, multiple pods are being hidden by services. For the same service, many pods can come and go out. Kubernetes service is persistent, can balance the loads, and provide VIP layer and discovery. It identifies pods by the label selector.
The location where the containers can access and store the information is called volume. If a container is destroyed its files get lost. When containers run in a single pod then it becomes difficult to share files between those containers. For applications volume work is part of a local file system that can be backed by another storage backend.
Grouping mechanism is known as a Namespace that can group services, pods, replication controllers, and volumes. A degree of isolation from other system part is provided to the clusters. Namespaces can divide cluster resources between multiple users.
This Kubernetes Tutorial gives you a sound idea of concepts like what is Kubernetes, features, architecture, and more. But it is not complete if we are not sure of key terminologies.
Moving ahead to the Kubernetes Tutorial, we will discuss Kubernetes drawbacks.
Kubernetes is an ultimate tool for orchestration and microservice clustering. It is still under development and will surely bring lots of changes and improvements in a clustered infrastructure. A user can easily manage the network and clusters by using this wonderful automated tool. This Kubernetes Tutorial is just a beginner guide to help freshers with basic concepts like what is Kubernetes, its features, architecture, and more which would help you in getting closer to your goal of getting Kubernetes certification. To know more about the tool, you should join online Kubernetes training classes right away.
Read: Popular Tenets to Learn DevOps
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
A Quick Guide to Regression Testing in DevOps
![]() 5.6k
5.6k
DevOps Skills That Organization are Looking for DevOps Engineer
![]() 388k
388k
How to Learn DevOps and Become a DevOps Engineer | Complete Guide
![]() 431.4k
431.4k
DevOps Engineer Job Description: Roles and Responsibilities [2025 Updated]
![]() 449.3k
449.3k
What are the difference between Git Push and Git Push Origin?
![]() 17k
17k
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on DevOps Course
Interviews