Introduction
Do you keep facing a similar situation when trying to implement a TCP connection, everything seems fine from the server side, but when running the client program, you are facing an error, “java.net.connectexception: connection refused. Want to fix it? Keep reading!
Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused is the most frequent kind of networking exception occurring in Java. Typically, Java books don’t tell you how to handle these problems quickly. This is why we have compiled this comprehensive guide to help you with the exception that is helpful for Java professionals during network programming.
In this blog, we will discuss
- The reasons why Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error occurs
- How to fix Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error
- How online Java training will help you impart in-depth Java knowledge
Without further delay, let’s solve your Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error.
What is Java.net.ConnectException: Connection Refused Error?
The Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error comes when you try to make a TCP connection from the client to the server. A similar error may come during RMI (Remote Method Invocation) because the RMI method is also underneath the TCP_IP protocol.
Let’s know the reasons why the Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error occurs.
Why java.net.connect Exception Connection Refused Error Occurs
Do you know what is an exception in Java? An exception in Java is primarily an unexpected or exceptional event that occurs during program execution, in other words, during run time, and typically results in disruption of the program.
The network error “java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused” clearly states that the client is trying to make a TCP connection with the server and fails. Here are the possible reasons:
- Server or Client is not in a network: Either client or server or both of them are not in the network like LAN or internet; in that case, Java will throw an error - java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused.
- If the server is down: If the server is down or not working properly or there is a low network connection, in that case also Java will throw an error - java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused, you must be thinking, what do I do?
The most irritating thing to notice here is that the reasons are possibly different. Still, Java throws a single error in all possible scenarios that may be difficult to deal with the Java programmer. If there is any server issue, then you can check the status of the server with the command “ping,” or there are lots of similar options to get the response back from the port.
- The server is running but not listening to the port: The most typical case is when the server is running well but not listening to the port. This is the most advanced reason that could not be figured out quickly. The developer needs to check out the network configuration properly. In the case of hierarchical configuration, there are chances of overriding where default settings will override your actual settings.
- Firewall Restriction: If the network is protected by firewalls, then the same network error will be thrown by the Java programming language. Here, the Java developer needs to submit a request to the network administrator for continuous communication between IP addresses and the port. In case permission is not allowed by the firewall, then it will show the same error again and again.
- Incorrect host port combination: When you are working on networks, the most obvious terms you should know about are our host, port, MAC address, IP address, router, switch, etc. If you are unsure of any of the terms, then networking programming may be challenging for the developers. The next possible situation is the wrong combination of host and port number.
This is possible that you have provided either the wrong host or port number then the network will throw the same error again. Here the only solution is to check for active configuration settings and make necessary changes as required for successful communication.
- Server is stopped: Suppose a server administration gave some IP address and PORT to access the server. But he stopped the server, but if your client programs try to access the server with administrator-provided credentials, the client program will get the exception.
- Protocol mismatch: HTTP, RMI, Websocket, etc., uses TCP as the underlying protocol. HTTP request starts with
http://, and RMI protocol starts with rmi// or WebSocket protocol starts with ws://. If we request an HTTP request with rmi protocol, it will throw the java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused.
During a network connection, you have to make sure that the correct protocol has been passed as expected by the server. For RMI, Client-Server architecture, and HTTP, the most obvious protocol to establish a network connection includes TCP.
Want to brush up your Java knowledgebase, check out this tutorial that speaks at length about Java language, Java operators, and control flow.
Ways to Deal With java.net.connect Exception Refused Connect Error
In the above section, we have discussed all possible reasons closely. Here is the right time to approach a solution to deal with the “java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused” network error professionally.
- First of all, use the ping command to check if the server is connected to the port or not. If you are able to ping successfully without any error, then it shows that the client and server both are well connected, and the reason is somewhat different.
- In the second step, try to connect with the server and port with telnet. The “Telnet” command is an easy way to check connectivity to the server from a client. You would be able to know whether the problem is with the server or client code. Also, you would be able to know if the serving is running well or not.
- Check the configuration of the client that will tell you about the correct IP address and port number. For highly complex connections, you should try RMI calls so that you can be sure of the right protocol and the connection string. You can use the same process when using MySQL and JDBC.
Check firewall connections, and Windows firewall logs, and make sure that networks are accessible to each other to make successful communication. Also, you have to make sure that the source and destination computer should be on the same network, host, or router.
Let’s know how you can resolve the issue at the network layer. If you are sure about subnet creation, IP addressing, and routing, then this would be easy for you to solve the network issues correctly and quickly too.
Troubleshooting IPv4 Logical Addressing at Network Layer
To establish communication at the network layer, we need a global addressing scheme that is named as logical addressing in the network world. These logical addresses are referred to as IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. Although the IPv6 address scheme has been deployed into the network world, still many organizations rely on IPv4 addressing only.
This is the reason why every network engineer should know how to troubleshoot IPv4 logical addressing on devices. Online Java training selfpace will help Java developers master different Java programming skills. Technical issues may be faced by network engineers while troubleshooting IPv4 like bad address, subnet mask or default gateway address, etc.
When IPv4 addresses are deployed on devices, they are assigned dynamically through the DHCP protocol. The next topic of interest is Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is required to translate IPv4 logical addresses to public addresses that can be further routed on the internet.
This adds another complexity to the environment as you need to know how to troubleshoot NAT so that devices can be accessed quickly, even externally to the organization. This is true that we are using IPv4 as of now, but soon there will come a time when IPv6 address schemes will be deployed in the organization.
So you should also know how to troubleshoot IPv6 successfully. In future tutorials, we will discuss IPv6 addressing schemes, addressing technologies, and their troubleshooting tricks in deep that can help you in starting a successful Java development career with organizations. As of now, we are limited to troubleshooting tricks for IPv4 logical addressing at the network layer.
Troubleshooting IPv4 Addressing
Here, we will focus on a deep understanding of IPv4 addressing and how to check whether each of the devices is addressed correctly on the network or not.
IPv4 Addressing Issues
Every IPv4 address comprises two major parts – one network/subnet mask and the other is the host part. When two devices want to communicate together, then it is necessary that both of them should share the same network/subnet mask.
In case, the subnet mask for both of the systems is different then it will notify back with addressing issues that need to be troubleshot by a network engineer.

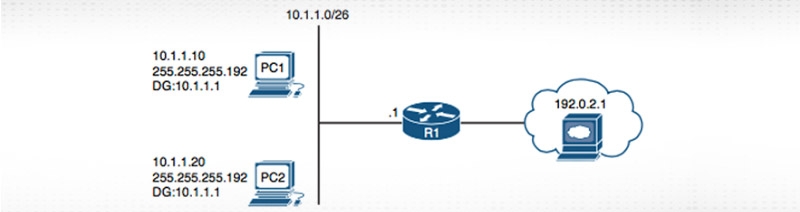
Figure-1 Correct IPv4 Addressing Example
In the given figure, the sample subnet for both PCs is (10.1.1.0/26) and they are sharing default gateway R1. Let us discuss on the network addressing how it works actually. Take an example where PC1 wants to communicate with PC2. In that case, it will start for DNS lookup to know the IP address for the PC2. After DNS lookup, IP address 10.1.1.20 is returned.
Now, PC1 will check whether PC2 is located on the same network or they are sharing the same subnet mask or not. For this purpose, it will convert the Decimal number to Binary to get accurate results.

As you can see both binary bits are exactly the same, so it is clear that PC1 and PC2 share the same network and packets can be exchanged directly without any need of default gateway R1. In technical words, PC1 will create a MAC address of its own system as the source and MAC address For PC2 as the destination. Here’s how you can get MAC address from IP1.
Now let us see what happens when PC1 wants to communicate with a web server (192.0.2.1). It will again start for DNS lookup to know the IP address of the web server. After DNS lookup, IP address 192.0.2.1 is returned. Now, PC1 will check whether PC2 is located on the same network or they are sharing the same subnet mask or not. For this purpose, it will convert the Decimal number to Binary to get accurate results.

As you can see that both binary bits are not exactly the same, so it is clear that PC1 and the web server don’t share the same network, and packets cannot be exchanged directly. Here, you need the default gateway R1 to establish the communication further. In technical words, PC1 will create the MAC address of its own system as the source and the MAC address of the web server as the destination.
The above discussion makes sure that the correct IP address is paramount for success. Now the question comes as to what will happen if PC1 is configured with the wrong subnet mask by mistake. This is given in the following figure.
The above discussion makes sure that correct IP address is paramount for success. Now the question comes to what will happen if PC1 is configured with the wrong subnet mask by mistake. This is given in figure 9-2.

Figure-2 Incorrect IPv4 Addressing Example

After comparison PC1 concludes that PC2 is not on the same network and it needs to route the packets to the default gateway R1. SO, it will create a MAC address of its own system as the source and a MAC address of the default gateway R1 as the destination.
As a result, the packets will be addressed to the wrong device even if both of the systems were connected to the same network only. This is an example of Incorrect IP addressing that needs to troubleshoot further by a network engineer. Not only an improper subnet mask will cause issues, but improper IP addressing along with a right subnet mask will also cause connectivity issues.
Additionally, if the default gateway is not configured correctly, then it will route the packets to the wrong destination that is not acceptable to any of the organization. Being a troubleshooter or network engineer, you should be aware of all possible connectivity issues, you may face during network configuration.
If you are aware of all possible situations only then you can resolve the issues quickly. The IP information can be verified on Windows PC with "ipconfig" command and you can check the same details on a router or switch with show IP interface inter- face_typeinterface_number command.
Do you Know How to Determine IP Addresses Within a Subnet?
Here is a quick tour that will help you determine IP addresses within a subnet. Figure 9-3 “Determining IP Address within a Subnet,” will give you a clear idea of how they are actually assigned.

Figure-3 Determining IP Address within a Subnet
Take the last octet of the subnet mask and subtract it from 256. In this case, the last octet is 192 and when it is subtracted from 256, the result would be 64. So the subnet for this network can be defined as 10.1.1.0/26 to 10.1.1.63/26. The next subnet would be 10.1.1.64/26 to 10.1.1.127/26. The third subnet would be 10.1.1.128/26 to 10.1.1.191/26 and so on.
Let’s look at some frequently asked questions and answers to solve all your queries related to Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error.
Java Certification Training Online
- Personalized Free Consultation
- Access to Our Learning Management System
- Access to Our Course Curriculum
- Be a Part of Our Free Demo Class
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is ConnectException Java?
Ans: ConnectException Java is one of the most common Java exceptions, related to networking. It signals when an error occurred while attempting to connect a socket to a remote address and port.
Q2. What does java net connectException refused mean?
Ans: Generally, connect refused errors occur in a connect system call when an application attempts to connect through TCP to a server port that is not open. In simple words, connection refused means the port you are trying to connect to is not open. There may be different reasons- you may be connecting it to the wrong IP address, or to the wrong port or the server is not in the run or is listening on the wrong port.
Q3. Why do we get java. net connectexception connection refused connect error?
Ans: Here are the two most common causes we get connection refused:
Misconfiguration: It happens when you mistype the port number or use stale info about what port the service they need is running.
Service Error: The service that should be listed on a port has crashed or is unavailable.
Another cause may be that a firewall along the way has been configured with a rule to refuse access to the service.
Q4. What is the Java net ConnectException connection refused?
Ans: The Java connection refused is a case of a user trying to connect on TCP port but not able to access. There are many reasons, here are some possible causes why Java net ConnectException connection refused error occur:
- The server is not working
- The client is not in the network
- The server is not in the network
- Both are not in the network
Q5. How do you handle Java net ConnectException connection refused?
Ans: To resolve the Java net error, first try to ping the destination host, if you are able to ping the host means the client and server machine are in the proper network. Your next step should be connecting to the server host and port using telnet. If you find that you can connect with the server means there is no problem from your side, something is wrong with your client code.
Q6. How does Java handle java.net.connectexception?
Ans: ConnectException exception is a common Java exception in networking. You may find this issue when you try to set up a TCP connection from a client application to a server. Since this is a checked exception, you need to handle it in the proper way in your code.
Q7. hat does the Java.net ConnectException connection refused no further information mean?
Ans: The Java net ConnectException connection issues might occur due to a misconfiguration in the Minecraft server that the player is striving to join. It may also happen due to an underlying problem present on the client-side.
Q8. How do I fix Java net ConnectException connection refused No further information?
Ans: To fix the java.net.connectexception connection refused error-
- First, know the causes behind the refused error
- Then, power-cycle your network
- Reset your network configurations
- Add an exception in Firewall
- Add the IP address and Port before connecting
- Check for Port Filtering
- And at last, check ISP Network Access
Q9. How do you fix java.net connectexception connection refused Minecraft?
Ans: The java.net.connectexception connection refused error in Minecraft is related to a network, it appears when your network blocks the connection to the server. By adding Minecraft and its launch to your Firewall and Antivirus exceptions and making sure your network’s firewall is open to send and receive the port 25565, you can fix java.connectexception connection refused Minecraft error.
Q10. How will online Java training help in my Java developer career?
Ans: Learning about the root cause and solutions can help a Java developer carry out all his roles and responsibilities smoothly. You can enroll in a professional Java course to learn about exception handling. You might also get questions about these errors in core Java interview questions. For Java developers plenty of job opportunities are available and if you are a fresher or an experienced professional, go through these top 110 Java interview questions and answers to prepare yourself for the interviews.
Conclusion
Have you got your solution to Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error? Getting such errors is common, but knowing the solution and the main cause can make the process of resolving them easier. Employers want their developers to be efficient and smart enough to have such knowledge.
Save this blog to use all the tricks the next time you get stuck with Java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused error. If you want to learn more about networks and Java to become an efficient Java developer, you need professional online Java training, and Janbask Training offers exactly that. What are you waiting for? If you have the passion and interest to learn Java and make a career with it, join the Java course now.
Java Course
Upcoming Batches
Trending Courses
Cyber Security
- Introduction to cybersecurity
- Cryptography and Secure Communication
- Cloud Computing Architectural Framework
- Security Architectures and Models
Upcoming Class
-1 day 15 Sep 2025
QA
- Introduction and Software Testing
- Software Test Life Cycle
- Automation Testing and API Testing
- Selenium framework development using Testing
Upcoming Class
6 days 22 Sep 2025
Salesforce
- Salesforce Configuration Introduction
- Security & Automation Process
- Sales & Service Cloud
- Apex Programming, SOQL & SOSL
Upcoming Class
3 days 19 Sep 2025
Business Analyst
- BA & Stakeholders Overview
- BPMN, Requirement Elicitation
- BA Tools & Design Documents
- Enterprise Analysis, Agile & Scrum
Upcoming Class
3 days 19 Sep 2025
MS SQL Server
- Introduction & Database Query
- Programming, Indexes & System Functions
- SSIS Package Development Procedures
- SSRS Report Design
Upcoming Class
3 days 19 Sep 2025
Data Science
- Data Science Introduction
- Hadoop and Spark Overview
- Python & Intro to R Programming
- Machine Learning
Upcoming Class
10 days 26 Sep 2025
DevOps
- Intro to DevOps
- GIT and Maven
- Jenkins & Ansible
- Docker and Cloud Computing
Upcoming Class
1 day 17 Sep 2025
Hadoop
- Architecture, HDFS & MapReduce
- Unix Shell & Apache Pig Installation
- HIVE Installation & User-Defined Functions
- SQOOP & Hbase Installation
Upcoming Class
10 days 26 Sep 2025
Python
- Features of Python
- Python Editors and IDEs
- Data types and Variables
- Python File Operation
Upcoming Class
4 days 20 Sep 2025
Artificial Intelligence
- Components of AI
- Categories of Machine Learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks
- Recurrent Neural Networks
Upcoming Class
18 days 04 Oct 2025
Machine Learning
- Introduction to Machine Learning & Python
- Machine Learning: Supervised Learning
- Machine Learning: Unsupervised Learning
Upcoming Class
31 days 17 Oct 2025
Tableau
- Introduction to Tableau Desktop
- Data Transformation Methods
- Configuring tableau server
- Integration with R & Hadoop
Upcoming Class
10 days 26 Sep 2025




























Louis Anderson
I got confused about how to deal with this connection issue. Thank god, I could check your article. It is easy to understand and has all the points one may need to know the causes and deal with the error.
JanbaskTraining
It’s our pleasure to know, this post could help you. Feel free to comment if you face any further issue.
Maximiliano Jackson
Just finished reading this blog and got the idea how I can resolve the connection refused error in Java. Thanks for sharing it!
JanbaskTraining
Perfect!! For any queries, you can write us a mail, we will be happy to help you.
Paxton Harris
This is such an awesome post! I spent almost one and half hours getting each and every concept clearly and writing down major questions for recall. Thank you!
JanbaskTraining
You are welcome! Keep coming back to our site to read such value adding content.
Nash Martin
This information is so useful for someone facing the ava.net Connectexception connection refused error and looking for an instant solution.
JanbaskTraining
Yup, the purpose of this post is to present a quick guide to resolve the connection error.
Lane Clark
Wow, such a mindblowing post! You have explained in a simple way how to resolve the Java.net Connectexception connection refused error.
JanbaskTraining
Thanks for your encouraging words! Keep coming back to us for more such amazing content.
Josue Rodriguez
Thank you for sharing the complete overview on the Java.net Connectexception connection refused error. I have been searching for such informative guidance for a long time. Thanks a lot!
JanbaskTraining
Glad to hear, hopefully, you found it helpful.
Rafael Lewis
Hi Thanks for the info. I found this guide as the easiest option on connection refused error solution free. It has become very easy to resolve the errors after going through such a descriptive review blog as you can easily check them.
JanbaskTraining
We will try to bring more such helpful guidance.
Riley Walker
Must say, this is a superb post with all the required information one may need while resolving connection errors in Java. Thank you so much for sharing!!
JanbaskTraining
Wow! This is quite encouraging to hear.
Beckham Allen
I have always loved the way you present the difficult and lengthy piece of content in such an interesting and easy to understand way. Thanks for this amazing new post!
JanbaskTraining
You are always welcome! Write to us for any queries or confusions.
Jaden Hernandez
It’s a great, fully, interesting blog!! Thank you for sharing the Connection refusal error solving Blog !!
JanbaskTraining
You are welcome. Feel free to comment below for any doubts or queries.