19
SepGrab Deal : Upto 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
The collection is the type of variables that can store multiple numbers of records. It can increase and decrease dynamically.
It creates a new instance of the List class. A list can hold elements of any data type. A list is an interface. A list is an ordered collection of typed primitives, sObjects, user-defined objects, Apex objects or collections that are distinguished by their indices. A list is an ordered collection so use list when you want to identify the list element based on Index Number. The list can contain Duplicates. A list should be declared with “List” keyword. To define a list use list keyword by primitive data, sObject within <> characters. The index position of the first element in a list always starts with [0].it can grow dynamically at the run. It allows duplicate and null values.
Learn Salesforce in the Easiest Way

add(listElement) Example:
Read: A Basic Overview for Salesforce Security
|
||||||
|
From the index number, we can find the Name
Listmylist = new List();
string n1= ‘Daniel’;
string n2= ‘Philips’;
string n3= ‘Josh’;
string n4=’ Michel’;
string n5=’ Samuel’;
mylist.add(n1);
mylist.add(n2);
mylist.add(n3);
mylist.add(n4);
mylist.add(n5);
listallName= new list();
allName.addall(mylist);
string name=mylist.get(1);
system.debug(name);.//Philips
 Click on Debug result
Click on Debug result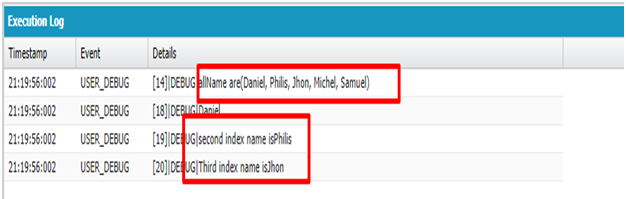 addAll(from List): Addall of the elements in the specified list to the list that calls the method. Both lists must be of the same type.
addAll(from List): Addall of the elements in the specified list to the list that calls the method. Both lists must be of the same type.
public class ExampleOfList { public static void addAlltest() { ListfirstList = new List (); firstList.add('Justin'); firstList.add('FRANK'); firstList.add('LOUIS'); for(string name1:firstList){ System.debug('First List Details is-->'+ ''+name1); } system.debug('First List size is-->'+ firstList.size()); List secondList = new List (); secondList.add('ALBERT'); secondList.add('JACKSON'); secondList.add('FREDDIE'); secondList.addAll(firstList); system.debug('Both list names are '+' '+secondList+''+secondList.size()); for(String name : secondList){ System.debug('Second List Details is-->'+ ''+name); } } } Salesforce Training For Administrators & Developers
- No cost for a Demo Class
- Industry Expert as your Trainer
- Available as per your schedule
- Customer Support Available
Debug result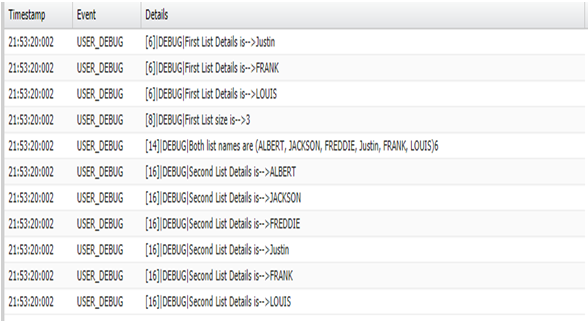 Remove (): It removes the list element stored at specific index, returning the element that was removed
Remove (): It removes the list element stored at specific index, returning the element that was removed
Read: Salesforce Administrator | Salesforce Admin Skills, Importance & How to Become a Salesforce Admin
List firstList = new List();
firstList.add('FREDDIE');
firstList.add('JACKSON');
firstList.add('ALBERT');
firstList.remove(2); //remove 2nd position value.
for(String name : firstList){
System.debug(name);
}
}
Debug result //ALBERT removed from list
List firstList = new List();
firstList.add('Justin');
firstList.add('FRANK');
firstList.add('LOUIS');
firstList.add('ALBERT');
firstList.add('JACKSON');
firstList.add('FREDDIE');
for(string name1:firstList){
System.debug('First List Details is-->'+ ''+name1);
}
firstList.sort();
system.debug('Names are in alphabate from '+' '+firstList);
Debug result CC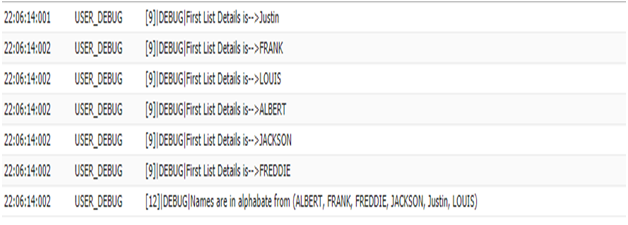 Clear (); This method removes all elements from a list, consequently setting the list size to zero.
Clear (); This method removes all elements from a list, consequently setting the list size to zero.
List firstList = new List();
firstList.add('Justin');
firstList.add('FRANK');
firstList.add('LOUIS');
firstList.add('ALBERT');
firstList.add('JACKSON');
firstList.add('FREDDIE');
for(string name1:firstList){
System.debug('First List Details is-->'+ ''+name1);
}
firstList.clear();
system.debug('list size is '+' '+firstList);
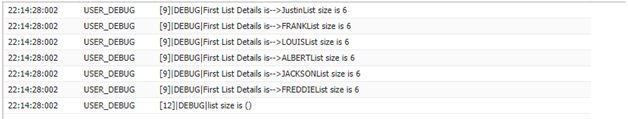 Clone ():
Clone ():
List firstList = new List();
firstList.add('Justin');
firstList.add('FRANK');
firstList.add('LOUIS');
firstList.add('ALBERT');
firstList.add('JACKSON');
firstList.add('FREDDIE');
for(string name1:firstList){
System.debug('First List Details is-->'+ ''+name1);
}
List secondList = new List();
secondList=firstList.clone();
system.debug(secondList);
 Equals(List); Compares the list with the specific list and returns true if both are equals, otherwise, returns false.
Equals(List); Compares the list with the specific list and returns true if both are equals, otherwise, returns false.
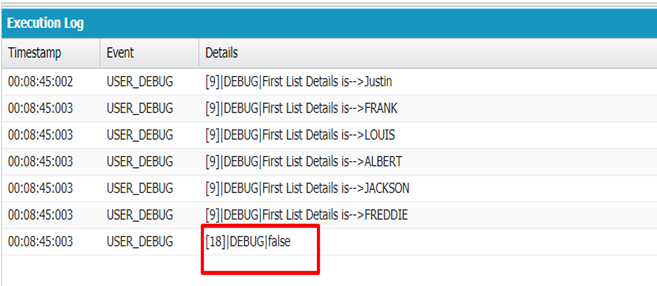
List firstList = new List();
firstList.add('Justin');
firstList.add('FRANK');
firstList.add('LOUIS');
firstList.add('ALBERT');
firstList.add('JACKSON');
firstList.add('FREDDIE');
for(string name1:firstList){
System.debug('First List Details is-->'+ ''+name1);
}
List secondList = new List();
secondList.add('Justin');
secondList.add('FRANK');
secondList.add('ALBERT');
Boolean result;
result=secondList.equals(firstList);
system.debug(result);
 addAll(Set) : Add all of the elements in specified set to the list that calls the method. The set and the list must be of the same type.
addAll(Set) : Add all of the elements in specified set to the list that calls the method. The set and the list must be of the same type.
Read: Interview With Eric Dreshfield
List listStrings = new List {'A', 'B', 'D', 'C'};
Set setString = new Set {'F', 'V', 'Z'};
listStrings.addAll(setString);
system.debug(listStrings);
Debug output is |DEBUG| (A, B, D, C, F, V, Z)
Example How to display selected record in another section using list Apex class
public class listDemoEx {
public List accList {get; set;}
public List selectedAccounts{get; set;}
public List getAccounts(){
if(accList == null){
accList = new List();
for(Account acc : [select Id, Name, Phone from Account limit 25]){
accList.add(new cAccount(acc));
}
}
return accList;
}
public PageReference processSelected(){
selectedAccounts= new List();
for(cAccount cCon : getAccounts()) {
if(cCon.selected == true){
selectedAccounts.add(cCon.con);
}
}
return null;
}
public class cAccount {
public Account con {get; set;}
public Boolean selected {get; set;}
public cAccount(Account c) {
con = c;
selected = false;
}
}
}

Apex is an intelligent programming platform for Salesforce. You can have a real fun with it by utilizing Collections. Share your creativity with us using the comment section below. Happy coding!
The JanBask Training Team includes certified professionals and expert writers dedicated to helping learners navigate their career journeys in QA, Cybersecurity, Salesforce, and more. Each article is carefully researched and reviewed to ensure quality and relevance.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Interviews