19
SepGrab Deal : Upto 30% off on live classes + 2 free self-paced courses - SCHEDULE CALL
Till a few years back, we used to visualize the SQL Server database being hosted in a physical server inside client premises. The database could remain in a single server or could span to multiple servers.
The advantage of an on-premise server is as follows.
But on-premise servers had a few drawbacks.
Cloud-based database systems are more flexible, reliable, and secured. The maintenance of the cloud-based system is less costly as most of the maintenance headache is taken by the vendor who is hosting the cloud. There are a few popular cloud hosting services for SQL.
We will discuss all these services in the next few paragraphs of this write-up.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Easy Implementation: A business will be able to run all its existing application and business processes without having to think about the technical problems in the backend. |
No longer in control: When we move the services to the cloud, we do not have any control over the data and application. |
|
Accessibility: Data can be accessed from anywhere via the internet. |
May not get all the features: There can be significant differences in the services each cloud service providers provide. |
|
No hardware is required: Since everything is hosted in the cloud so no need to maintain on-premise hardware. |
Still have to maintain servers: You still have to maintain server and IT staff for backup and recovery of data. |
|
Cost Per head: Overhead cost of technology is minimum. |
No Redundancy: A cloud server is not redundant nor it is backed up. There can be significant risk of loss of data if it crashes. |
|
Efficient Recovery: Cloud computing delivers faster and accurate retrieval of data. |
Bandwidth issues: For ideal performance, faster internet connection is required. |
We will now discuss the popular SQL Cloud hosting services one by one.
Microsoft SQL Server on AWS is a cloud service provided by Amazon. Using Amazon RDS for SQL Server it is very easy to set up, operate, and scale SQL Server deployments in the cloud.
It supports the “License Included” licensing model. It is not required to separately purchase Microsoft SQL Server licenses. "License Included" pricing is inclusive of software, underlying hardware resources, and Amazon RDS management capabilities.
Some of the features of Microsoft SQL Server on AWS are as follows.
It supports multiple instances, thus supporting almost any form of workload.
It is very easy to setup. It can be up and running with just a few clicks.
It is highly scalable, durable, and available while also being very simple to administer.
Supports a manual snapshot. This allows the user to take a backup of an entire database with a single snapshot.
Step 1
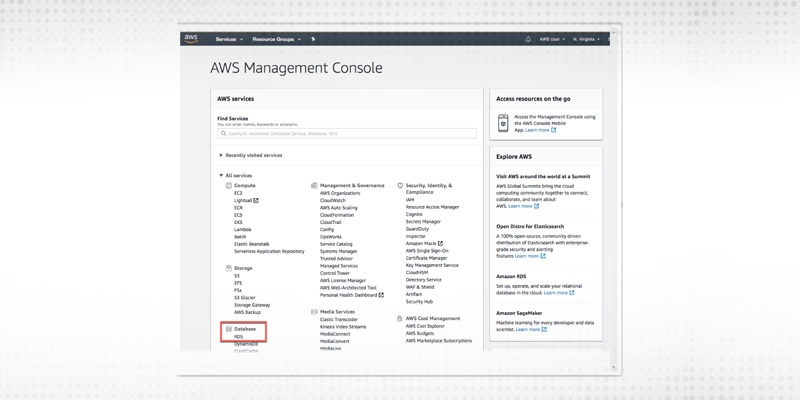
We need to first log into AWS management console. Then click on RDS under Database to open the Amazon RDS console.
Step 2
Next, we will use Amazon RDS to create a Microsoft SQL Server DB instance. This will have a storage capacity of 20GB and automated backups enabled. The retention period of the backup is one day.
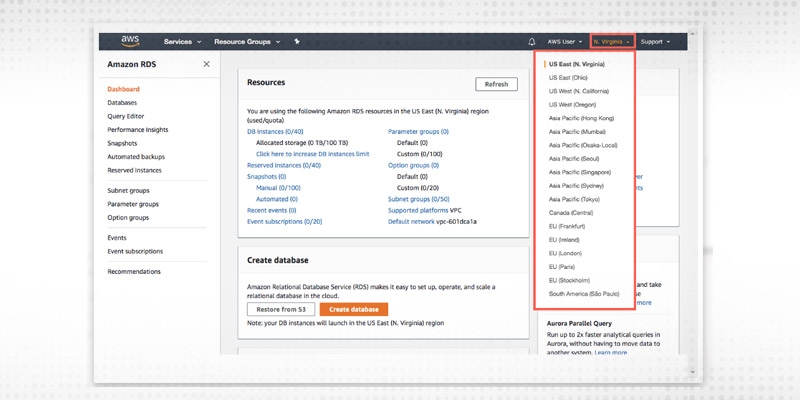
In the top left corner of the Amazon RDS console, we can change the region in which we want to create the database.
Step 3
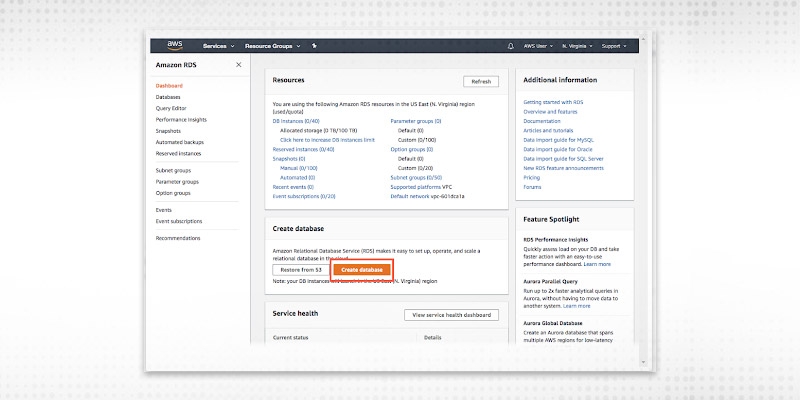
In the create database section we need to choose to create a database.
Step 4
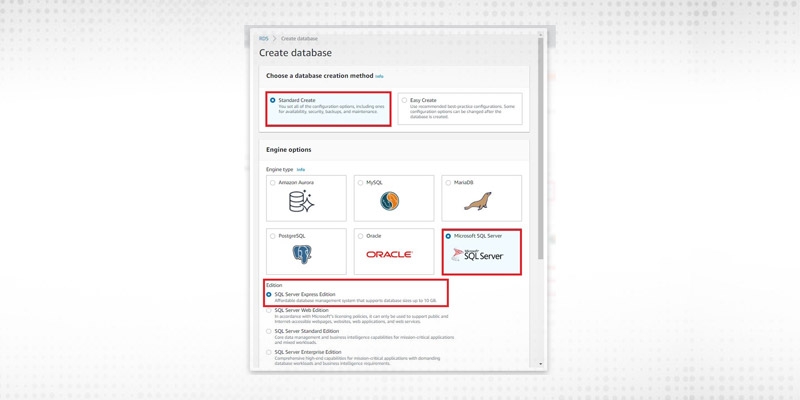
Next, we need to select the database engine. We select SQL Server Express here.
Step 5
Next, we configure the connectivity section.
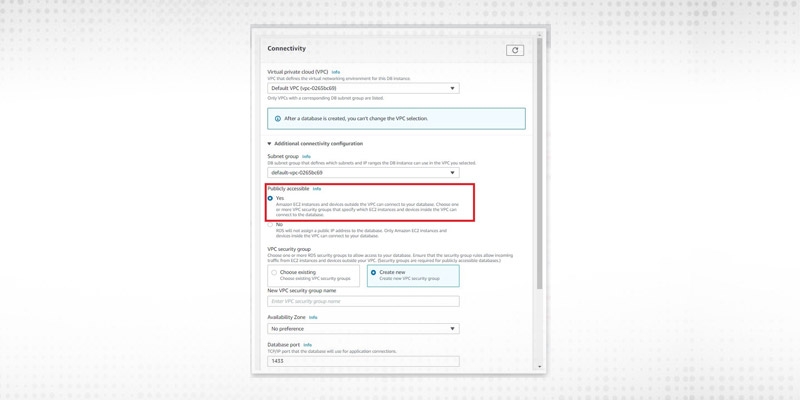

Click the Create Database button to create the database.
Step 6
Once the database is created we can view the database by clicking on view your DB instance.
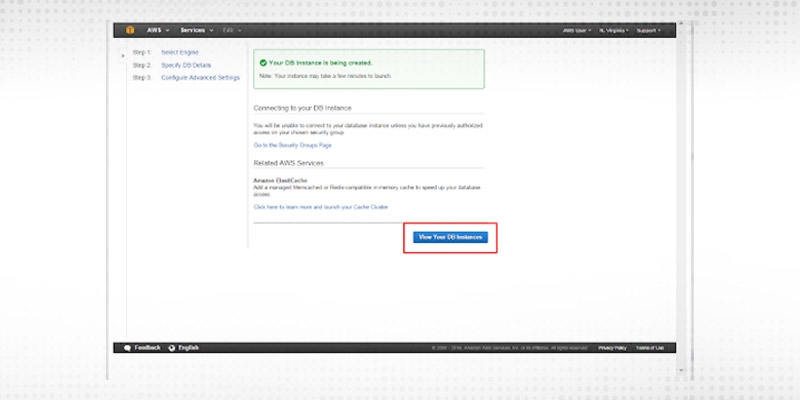
Step 1
Download and install SQL Client in the cloud following the below screenshot.
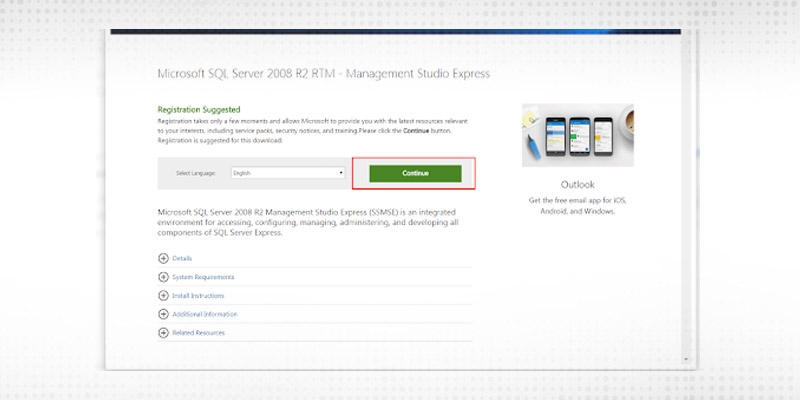
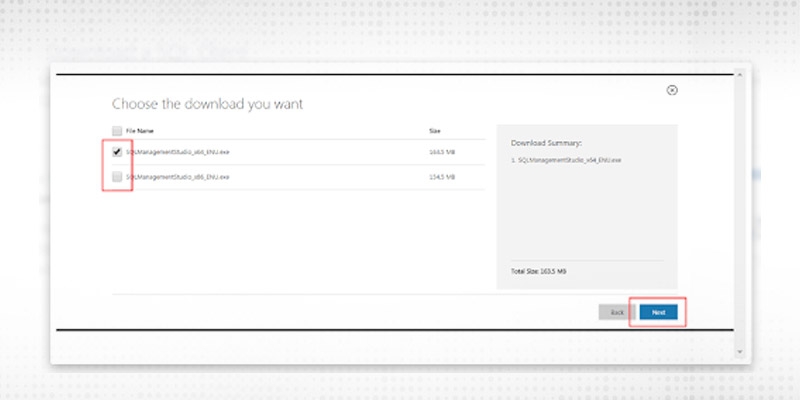
Step 2
Once the installation is complete, configure the client as below.
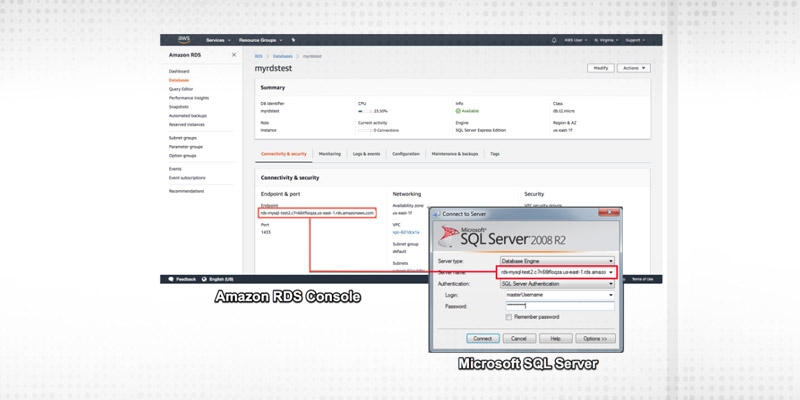
Click on the connect button.
Step 3
This will connect us to the database we have just created. We can now start creating tables and run queries inside the database using SQL Server Management Studio.
Google Cloud’s relational database offering is called Cloud SQL. It is a fully managed service designed to work with SQL Server. Cloud SQL is very similar to RDS, although it offers fewer database engines. It is highly available, scalable, durable, and very secure. Cloud SQL comes with automated backups for point-in-time recovery, and it integrates natively with other Google Cloud Services.
Some of the features of Cloud SQL are as follows
Create an instance of SQL Server in Cloud SQL
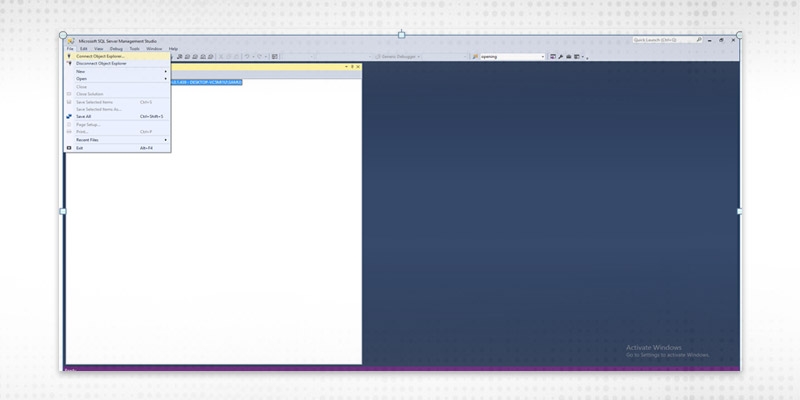
Step 1
In SSMS select connect to object explorer from the file menu.
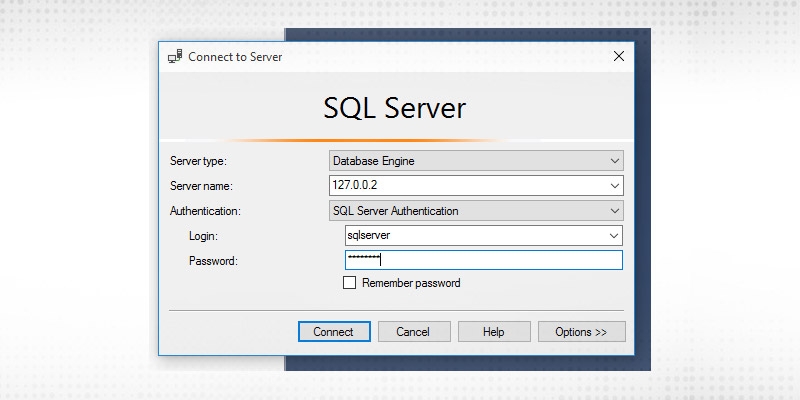
Step 2
Put the necessary configuration values and click on connect.
Step 1
In the SQL Server management Studio right-click on the database tab and click on new database.
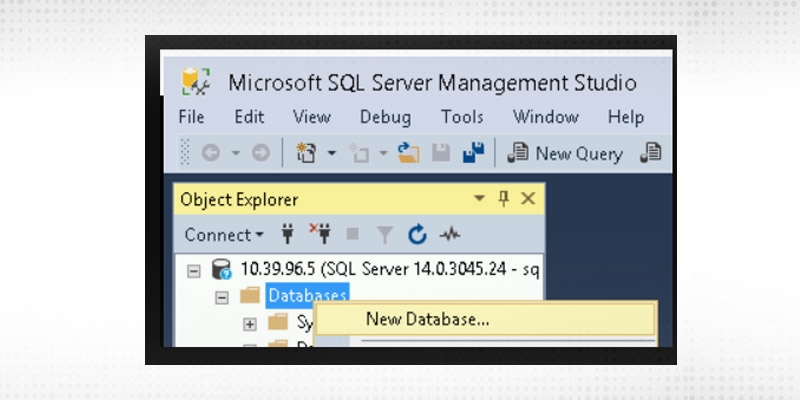
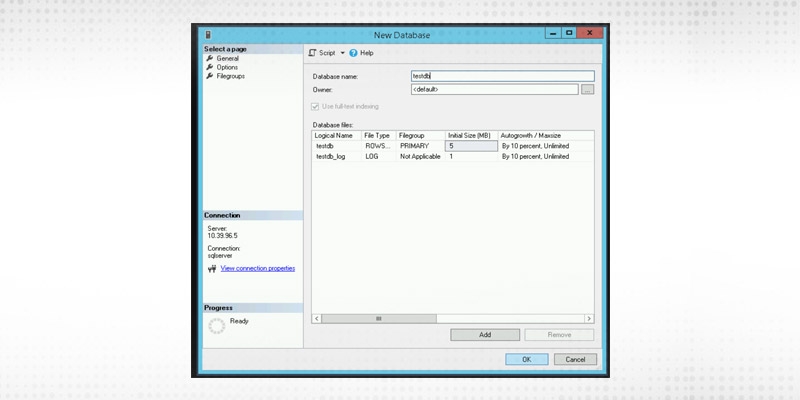
Step 2
We will name the new database as testdb. Click ok after that.
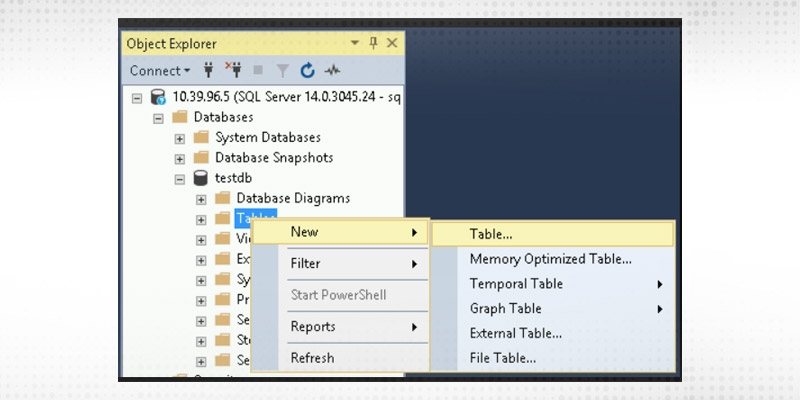
Step 3
Once the database is created select the testdb database. Expand and right-click on the tables tab and then new table. This would create a new table.
Step 4
Once the table is created, data can be inserted into the table using SQL insert statement.
Microsoft’s Azure is, at the moment, the second most commonly used public cloud provider.
Azure’s database services are similar to AWS’ RDS and Google Cloud’s Cloud SQL in that they are products for which maintenance is handled by the public cloud provider.
Some of the features of Microsoft Azure SQL Server Service are as follows:
Step 1
Sign in to the Azure portal.
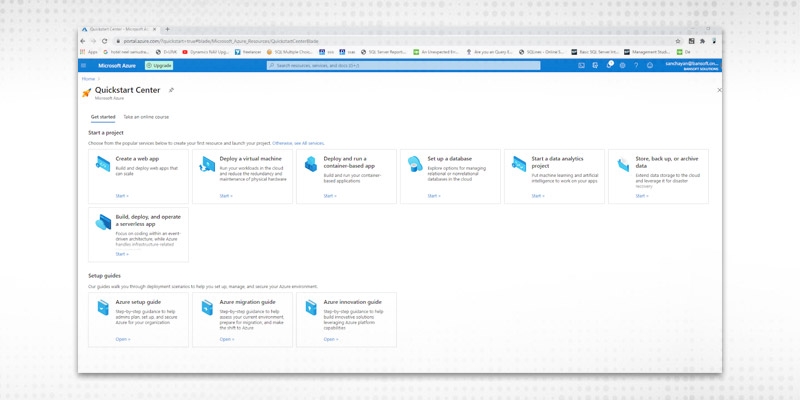
Step 2
Select Azure SQL on the left menu of the Azure portal. If Azure SQL is not in the list, select All services, and then enter Azure SQL in the search box.
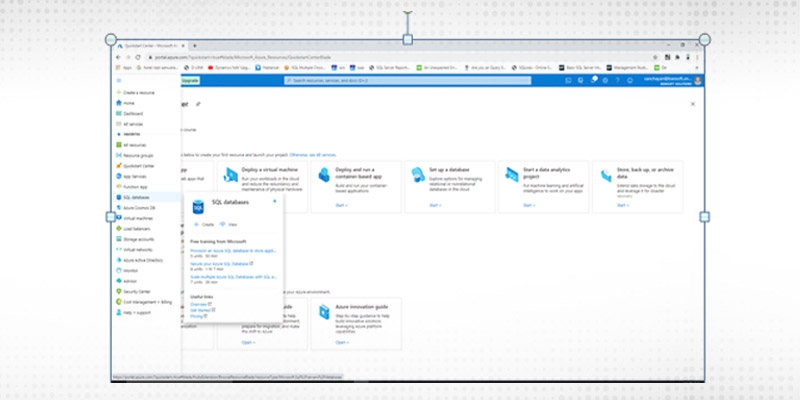
Step 3
Select +Add to open the Select SQL deployment option page. You can view additional information about Azure SQL Managed Instance by selecting Show details on the SQL managed instances tile.
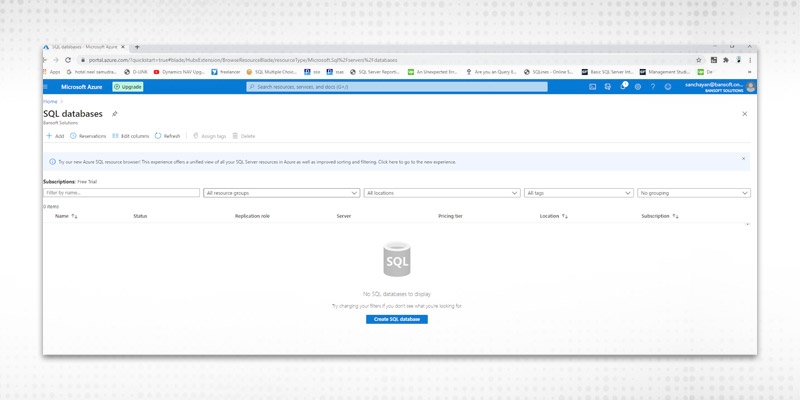
Step 4
Select Create Database.
Step 5
Fill in the minimum set of information under Basic tab.
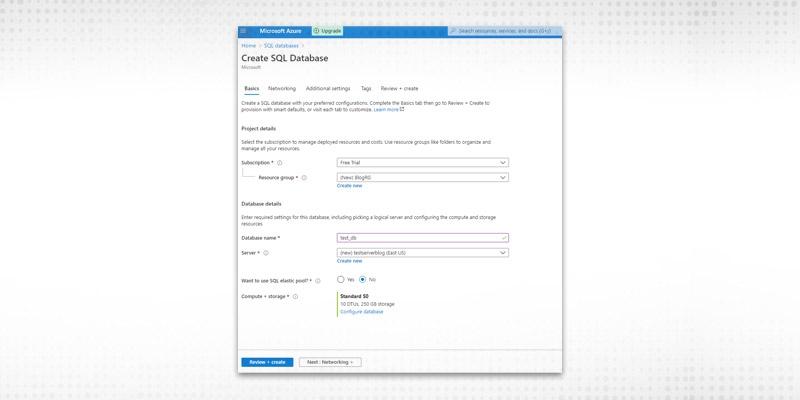
Click Review + Create
Step 6
The following screen appears.
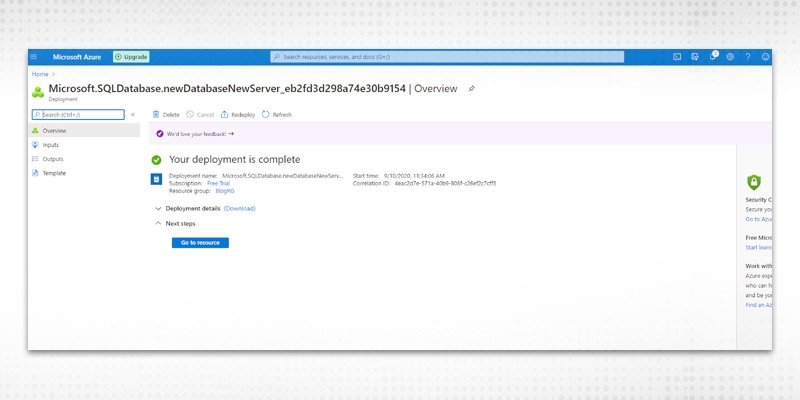
To view the Resources created click on Go To Resource.
Step 7
Click on the Resource Group name and the following screen appears.
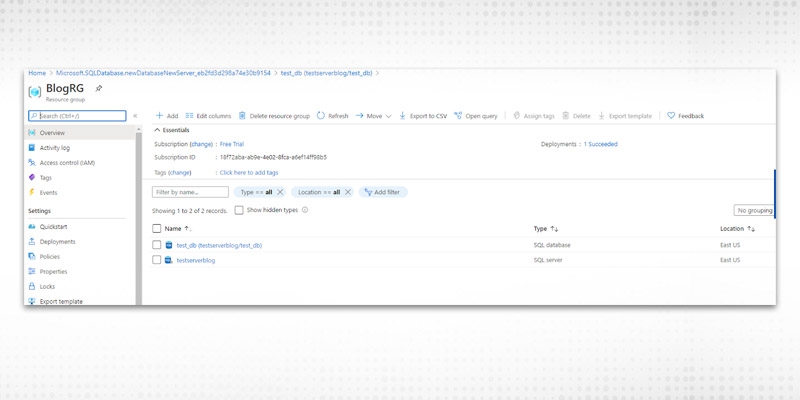
Step 1
Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and provide the necessary credentials.
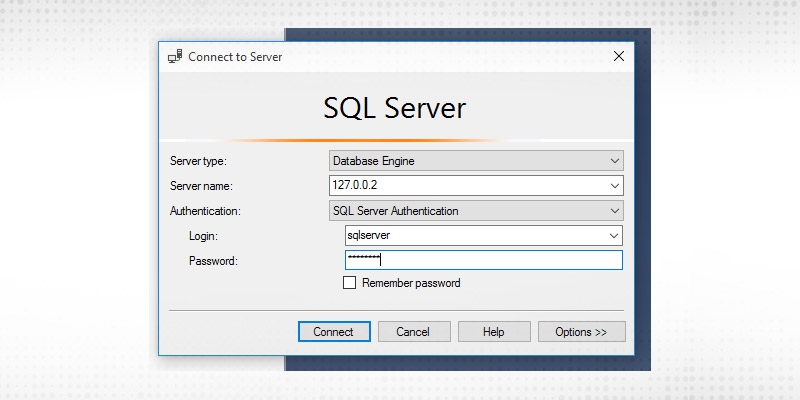
Click on Connect.
Step 2
The system connects to the Azure database.
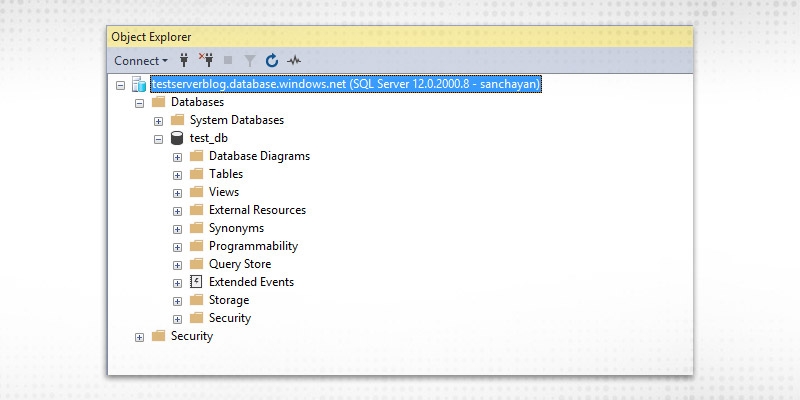
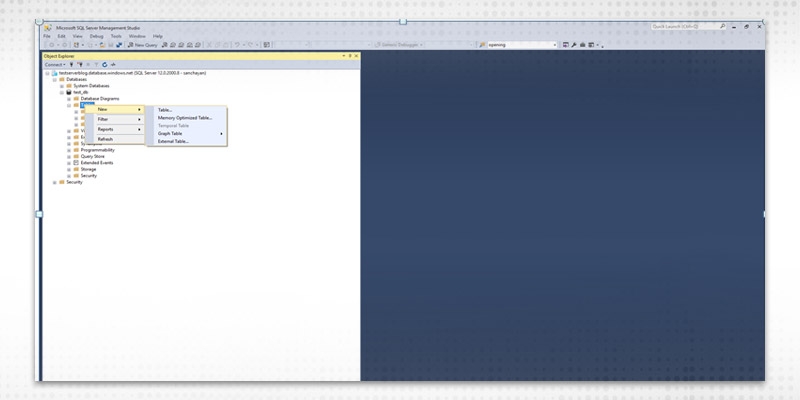
Step 1
Right-click on the Table tab under the database and click on new.
The above write-up gave an introduction to the three most popular SQL Services available in the market at this moment. As discussed above all these three services has some advantages and disadvantages over others. We had also discussed in the beginning the advantages and disadvantages of Cloud services as a whole at the very beginning of the write-up. Each of these services is suitable for a particular scenario. It is up to the users to decide which one of these services are best suited for their business.
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Email
Email
I love to learn new things and also like sharing my knowledge with others. As an experienced IT Professional I like to update myself constantly with new and upcoming technologies. The database management system is one of my favorite subjects which I constantly explore.

Cyber Security

QA

Salesforce

Business Analyst

MS SQL Server

Data Science

DevOps

Hadoop

Python

Artificial Intelligence

Machine Learning

Tableau
Search Posts
Related Posts
SQL Server Developer & Database Administrator Salary Structure
![]() 910.2k
910.2k
How to Prevent SQL Injection Attacks?
![]() 7.7k
7.7k
Normalization in SQL | 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF with Examples
![]() 489.9k
489.9k
OLAP vs OLTP: Key Differences, Architectures, Performance & Real-World Examples
![]() 459
459
How To Differentiate SQL Server JOIN, IN And EXISTS Clause?
![]() 788.6k
788.6k
Receive Latest Materials and Offers on SQL Server Course
Interviews